When it comes to selecting the ideal production method for your products or parts, two highly reliable options to consider are 3D printing services and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. While both techniques are capable of creating parts, it's essential to understand the significant differences that impact the final product and the entire process. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons of each approach, you can make an informed decision and choose the manufacturing technique that best aligns with your specific needs.
Understanding the Main Difference
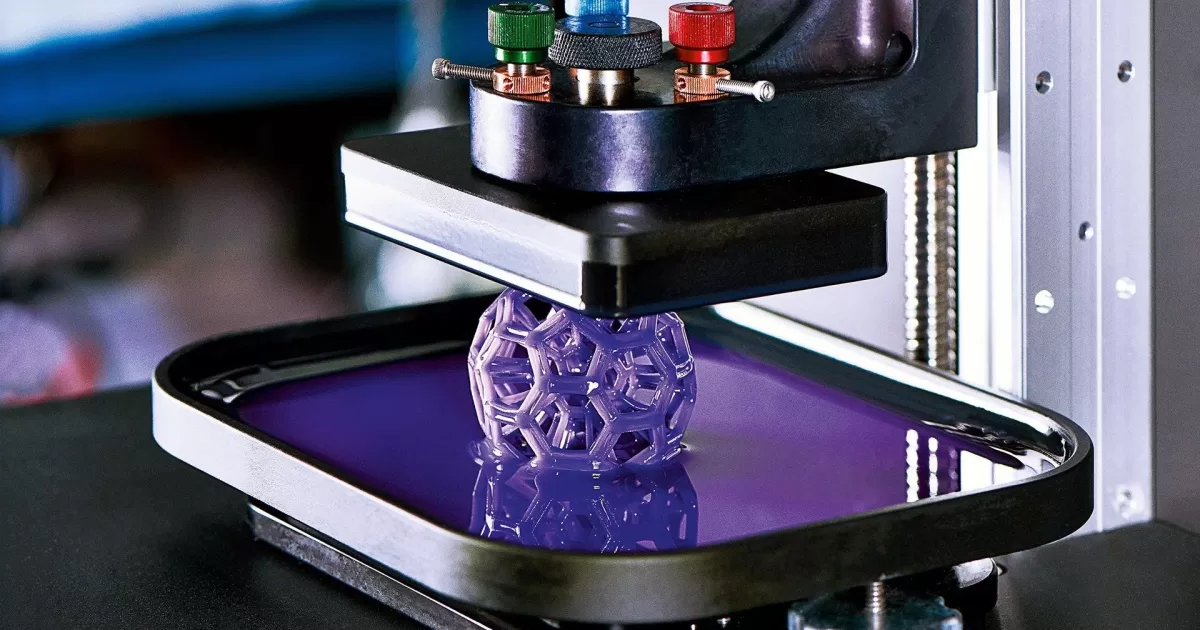
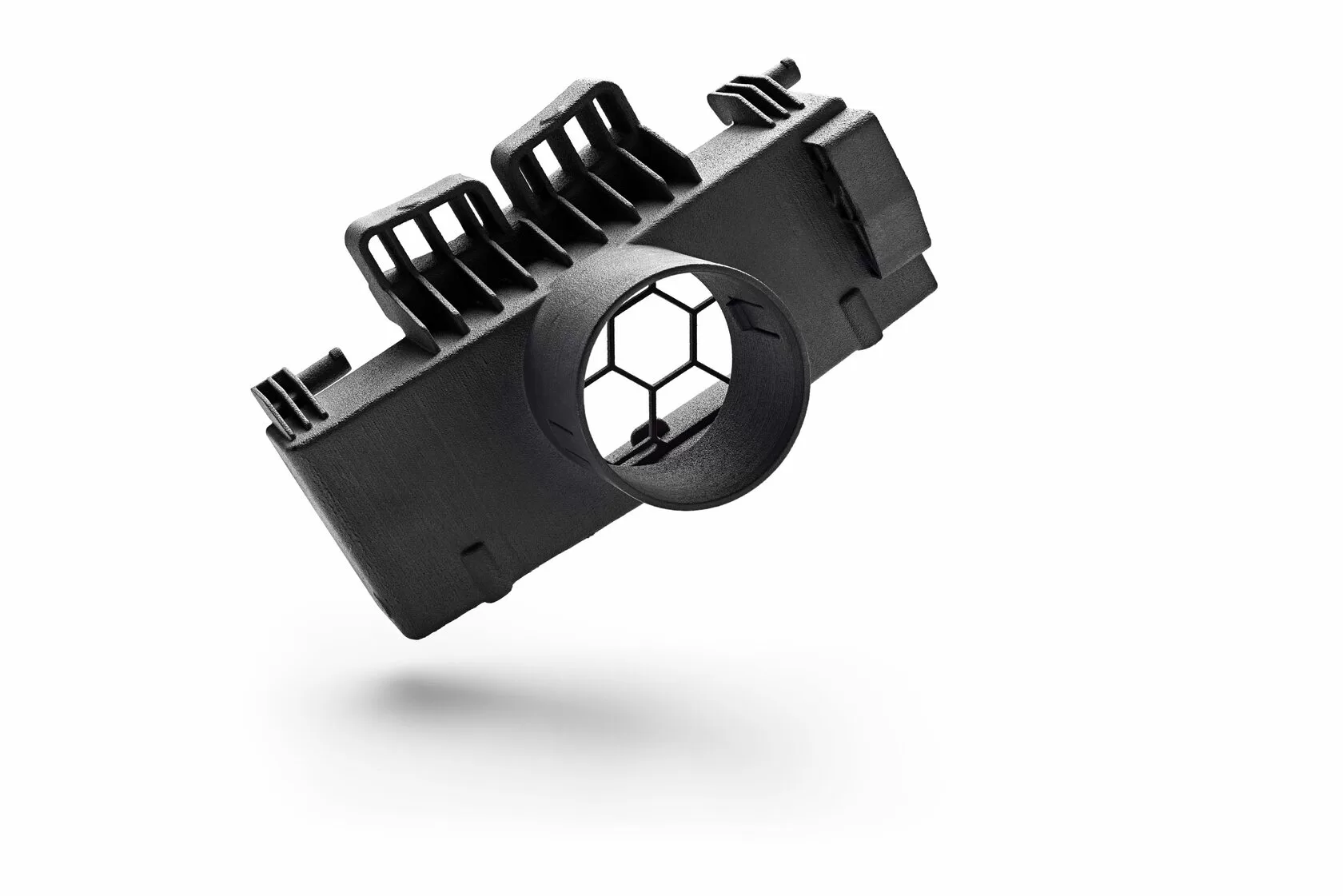
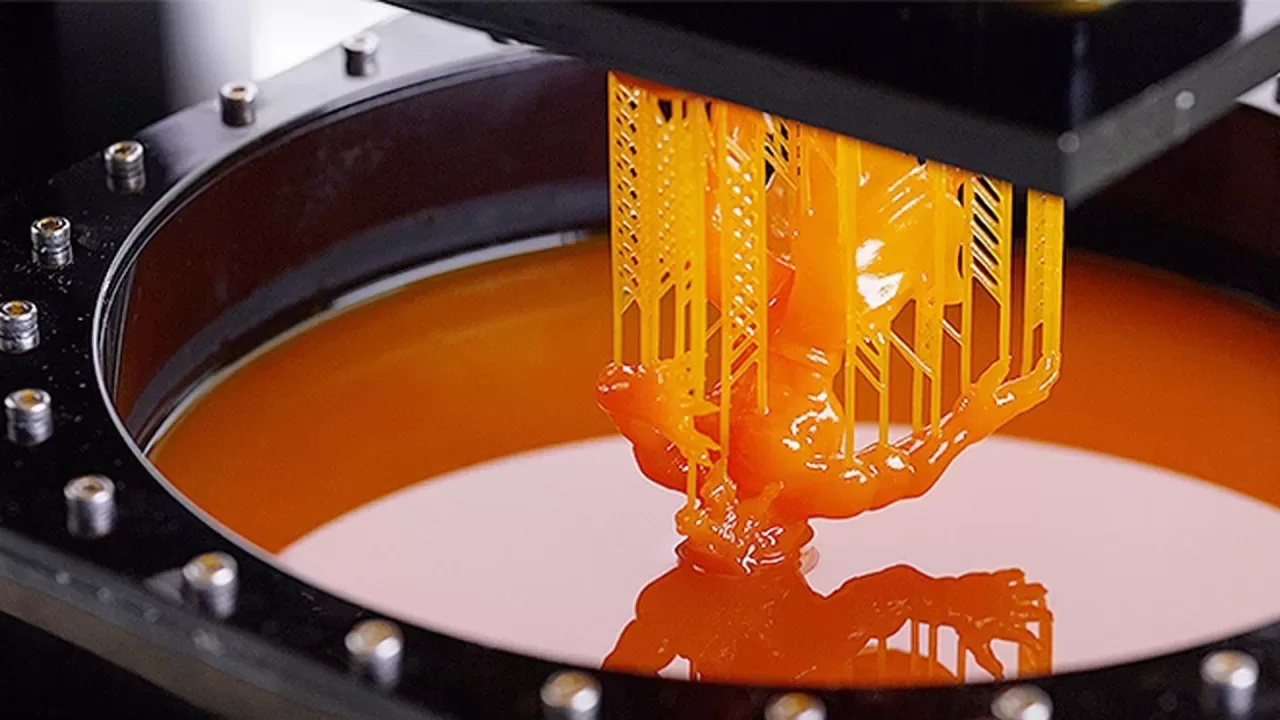
3D Printing: This method utilizes a 3D image to visualize the object before printing. The image is "sliced" into layers, and the object is printed layer by layer until the desired final product is obtained. With the constant addition of each layer during printing, this process is often referred to as "additive" manufacturing.
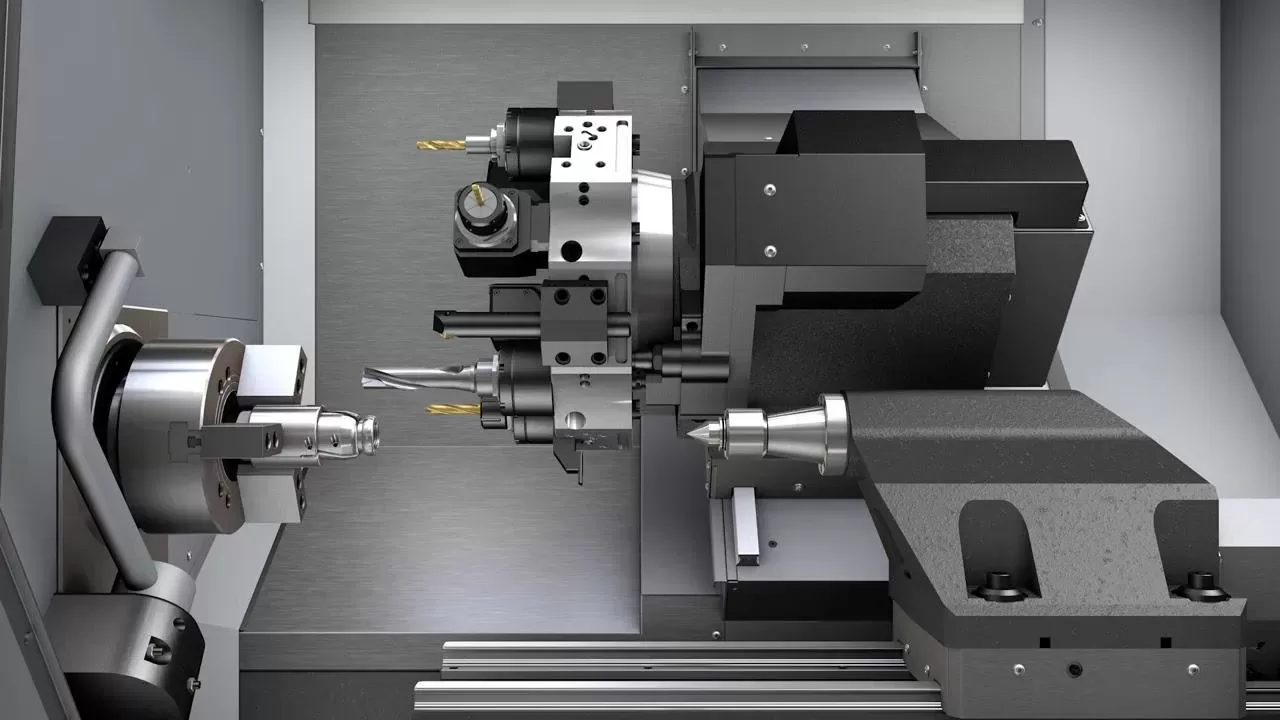
CNC Machining: In contrast, CNC machining starts with a large block of the chosen material. The block is placed on machinery equipped with sharp tools that cut away portions of the block to create the final product. Unlike 3D printing, which is additive, CNC machining is considered "subtractive" as it involves removing material from the block to shape the desired object.
Key Differences to Consider
Material Compatibility
3D Printing: This method commonly utilizes plastics such as filaments for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), polymer powder for Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and MultiJet Fusion (MJF) technologies, and resin for Stereolithography (SLA), among others.
CNC Machining: While CNC machining is frequently used for processing heavy metals, it can also work with various materials including plastics (as mentioned above), wood, and foam.
Production Process
3D Printing: This method offers a single-step manufacturing process that can operate without constant manual supervision, making it more cost-efficient compared to CNC machining. It is particularly recommended for producing smaller components for industrial use and customizable parts.
CNC Machining: Industries involved in the production of large-scale parts, such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and defense, find CNC machining highly valuable. However, it is a more labor-intensive approach as the machine requires manual setup.
Complexity of Objects
3D Printing: Advanced printing methods like SLS enable the manufacturing of precise and complex geometric objects, sometimes without the need for additional support structures commonly used in the printing process.
CNC Machining: Due to limitations in reaching all surfaces of the object, CNC machining may provide a lower level of precision compared to 3D printing. However, it consistently delivers parts of high quality.
Environmental Impact
3D Printing: As an additive process, 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the necessary materials. However, it consumes a significant amount of energy compared to CNC machining.
CNC Machining: The subtractive nature of CNC machining results in a considerable amount of unused material from the original block, requiring proper disposal. To reduce environmental impact, precision during the initial subtractive process can prevent the need for additional machining.
Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, the choice between 3D printing and CNC machining depends on various factors. Consider the type of object you need to produce, available manpower, budget, timeline, desired quality, and quantity. These considerations will guide your decision-making process. If you're searching for a reliable 3D printing company in China, feel free to contact us for a free, no-obligation consultation. We will help you explore the service that best suits your specific needs and requirements.




