CNC machines are incredibly versatile equipment, primarily due to the wide array of cutting tools they can handle. Familiarizing oneself with these cutting tools can aid in comprehending the fundamentals of CNC machining. From end mills to thread mills, a tool for every operation exists, enabling a CNC machine to perform various cuts and incisions in a workpiece.
Plus, a more thorough knowledge of machining can assist you in developing parts that are better suited for the manufacturing process.
This article examines some of the most commonly utilized CNC machining cutting tools, although there are numerous additional ones in existence beyond those mentioned.
What is a cutting tool?
A cutting tool is a device that removes material from a solid block. It's installed on the spindle of a CNC machine, which follows computer instructions to direct the cutting tool.
By using the process of shear deformation, cutting tools get rid of material from the workpiece. This means the sharp tool rotates at high speed and cuts many tiny chips from the workpiece, which then eject away from it. Some cutting tools only make contact with the workpiece at one point, whereas others, such as end mills, make contact at multiple points.
Most CNC machine cutting tools come with multiple flutes, which are helical grooves that run down the exterior of the tool. The flutes act as the troughs of the cutting tool, while the teeth, sharp ridges between each flute, are the peaks.As chips are ejected, they travel down the flutes.
The optimal number of flutes on a cutting tool depends on the material being worked on. For soft materials, a tool with fewer flutes is better as the wider flute allows for larger chips to be removed. However, for harder materials, a higher flute count may result in higher speed, but can cause chip jamming since each flute is narrower.
The cutting tool type affects the size of chips removed from the workpiece. Moreover, spindle speed and feed rate also impact chip size.
Cutting tool materials
To cut solid workpieces, cutting tools must be made from materials harder than the workpiece. As CNC machining is often used for parts made from very hard materials, this narrows down the available cutting tool materials.
Cutting tools play a crucial role in various industries, enabling efficient and precise machining processes. To optimize their performance, cutting tools can be enhanced with different coatings and materials. Let's explore some common coatings and their benefits:
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is an affordable alloy containing 0.6-1.5% carbon, along with silicon and manganese. It provides decent hardness and toughness for general-purpose cutting applications.
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
HSS is a more expensive option that offers superior hardness and toughness compared to carbon steel. It is achieved through the addition of chromium, tungsten, and molybdenum. HSS is ideal for demanding cutting operations.
Carbide
Carbide tools are made by sintering carbide with another metal, such as titanium. They are highly wear-resistant and heat-resistant, making them suitable for achieving excellent surface finishes.
Ceramic
Ceramic tools are utilized for cutting strong materials like superalloys and cast iron. They exhibit exceptional resistance to heat and corrosion, providing extended tool life in challenging applications.
Cutting Tool Coatings
Coatings can be applied to cutting tools to enhance their performance and extend their lifespan. Here are some common cutting tool coatings and their advantages:
Titanium Nitride (TiN)
TiN is a versatile coating with a high oxidation temperature. It increases the hardness of the cutting tool, enhancing wear resistance and reducing friction.
Titanium Carbo-Nitride (TiCN)
TiCN coating adds surface lubricity and hardness to cutting tools. It improves performance in high-speed machining and reduces tool wear.
Super-life Titanium Nitride (Al-TiN)
Al-TiN coating enhances the heat resistance of carbide cutting tools, particularly when minimal coolant is used. It ensures prolonged tool life even in demanding applications.
Diamond
Diamond coating provides excellent performance when cutting abrasive materials. It offers high hardness, low friction, and exceptional wear resistance.
Chromium Nitride (CrN)
CrN coating adds corrosion resistance and hardness to cutting tools. It protects the tool surface from wear and extends tool life.
By selecting the appropriate cutting tool material and coating, manufacturers can optimize their machining processes. Factors such as the material being machined, cutting conditions, and desired tool life should be considered when choosing the right combination. Consult with tooling experts to determine the most suitable cutting tools and coatings for your specific application requirements.
1、End mill
The end mill is the most widely used tool for vertical CNC machining. With cutting teeth at one end and on the sides, end mills can remove large amounts of material in a short space of time.
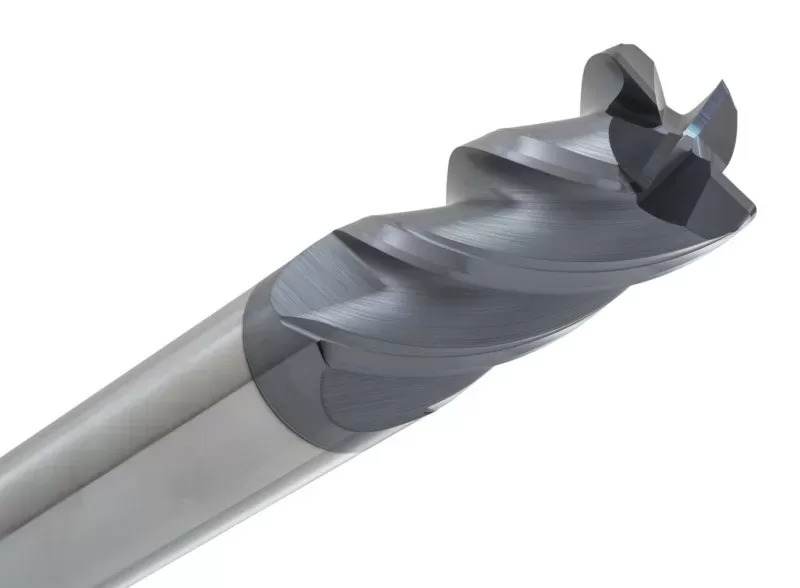

End mills come in many forms. Some have just a single flute, while some may have up to eight or even more. (Beyond four flutes, however, chip removal may become an issue.)
Types of end mill include:
- Flat: General purpose flat-faced tool suitable for 2D features
- Ball nose: Tool with ball-shaped end that is suitable for 3D contours and curves
- Bull nose: Tool with flat bottom and rounded corner suitable for fillets and roughing
2、Roughing end mill
Roughing end mills are designed specifically for rough machining operations, where the primary goal is to remove material quickly rather than achieving a smooth surface finish. These end mills feature multiple serrated cutting edges, which facilitate rapid material removal and efficient chip evacuation.
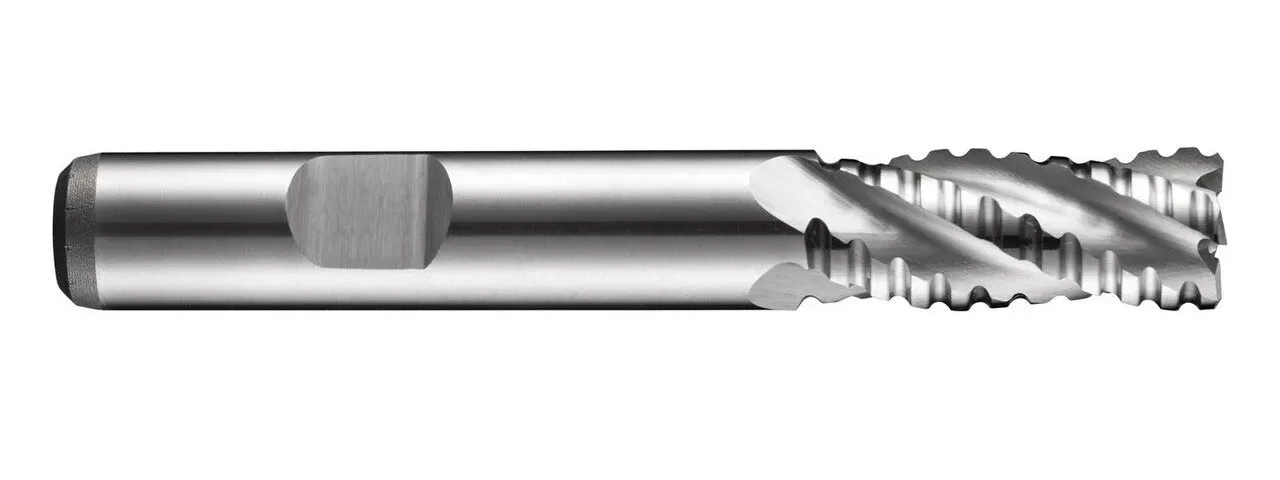
The serrated teeth of a roughing end mill are spaced apart, allowing for the efficient clearing of chips during the machining process. This design helps prevent chip clogging and reduces heat buildup, which can be beneficial when dealing with softer or more ductile materials that tend to produce longer chips.
Compared to standard end mills, roughing end mills are typically less precise in terms of achieving fine details and smooth finishes. They are primarily used for roughing or preliminary machining operations, where the focus is on removing larger amounts of material quickly and efficiently.
Roughing end mills are commonly made from high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide, which offer excellent durability and heat resistance. Carbide roughing end mills are particularly favored for their high hardness and ability to withstand the demands of aggressive machining.
When using a roughing end mill, it is important to consider the cutting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. These parameters should be optimized to achieve the desired material removal rate while maintaining tool life and minimizing vibrations.
Applications for roughing end mills can be found in various industries, such as manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and mold making. They are particularly useful when initial material removal is necessary, allowing subsequent operations with finer tools to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
In summary, roughing end mills are specialized cutting tools designed for aggressive material removal. They excel at quickly removing larger amounts of material, leaving a rough surface finish. By efficiently evacuating chips, these tools help maintain machining productivity and prevent tool damage. When used in the appropriate applications and with optimized cutting parameters, roughing end mills can significantly speed up the rough machining process while preserving the longevity of the tool.
3、Face mill
A face mill is a cutting tool used in machining operations to create flat surfaces on a workpiece. It is composed of a solid body with multiple interchangeable cutter inserts, typically made from carbide. The cutter inserts feature cutting edges on their sides, allowing for horizontal cutting.
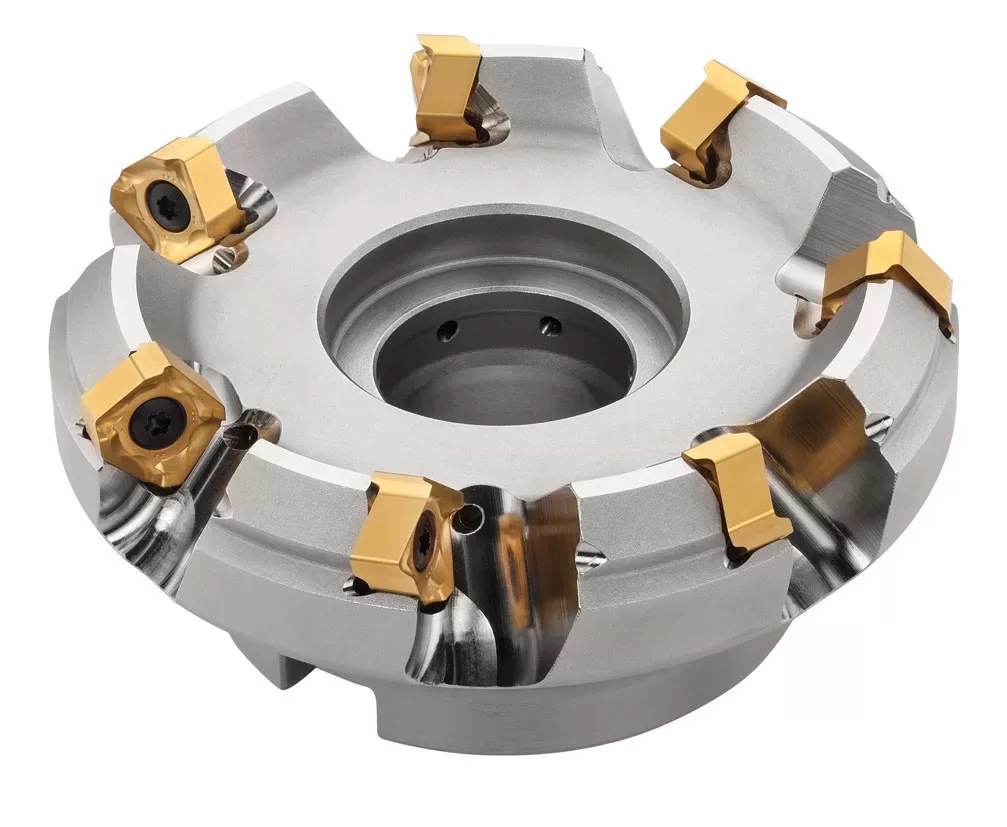

The primary function of a face mill is to remove material from the surface of the workpiece to create a flat section. This initial flat surface serves as a foundation for subsequent machining operations, where more detailed features or profiles are added using different tools.
One of the advantages of face mills is their cost-effectiveness. Instead of replacing the entire tool, variations in cutting profiles can be achieved by simply replacing the smaller cutter inserts. This makes it more economical compared to replacing the entire tool for different cutting requirements.
Face mills are commonly used in milling machines and machining centers. They are ideal for high-speed machining operations due to their sturdy construction and the ability to remove material quickly. The horizontal cutting action of face mills allows for efficient chip evacuation and reduces the chances of chip recutting, resulting in improved machining performance.
The choice of cutter inserts for a face mill depends on the specific application and material being machined. Different cutter geometries, coatings, and insert configurations are available to optimize performance for various materials, such as metals, plastics, or composites.
Face mills find applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, general machining, and metal fabrication. They are particularly useful in roughing operations, where large amounts of material need to be removed quickly to prepare the workpiece for subsequent machining steps.
In summary, face mills are versatile cutting tools used for creating flat surfaces on workpieces. They offer cost-effectiveness through the interchangeability of cutter inserts, allowing for flexibility in cutting profiles. With their horizontal cutting action and ability to remove material efficiently, face mills are valuable tools in the machining industry for achieving flat sections before proceeding with more detailed machining operations.
4、Fly cutter
A fly cutter is a cutting tool used in machining operations to create flat surfaces on a workpiece. It consists of a solid body that holds one or two tool bits. The tool bits of a fly cutter make broad and shallow cuts, resulting in a smooth surface finish.
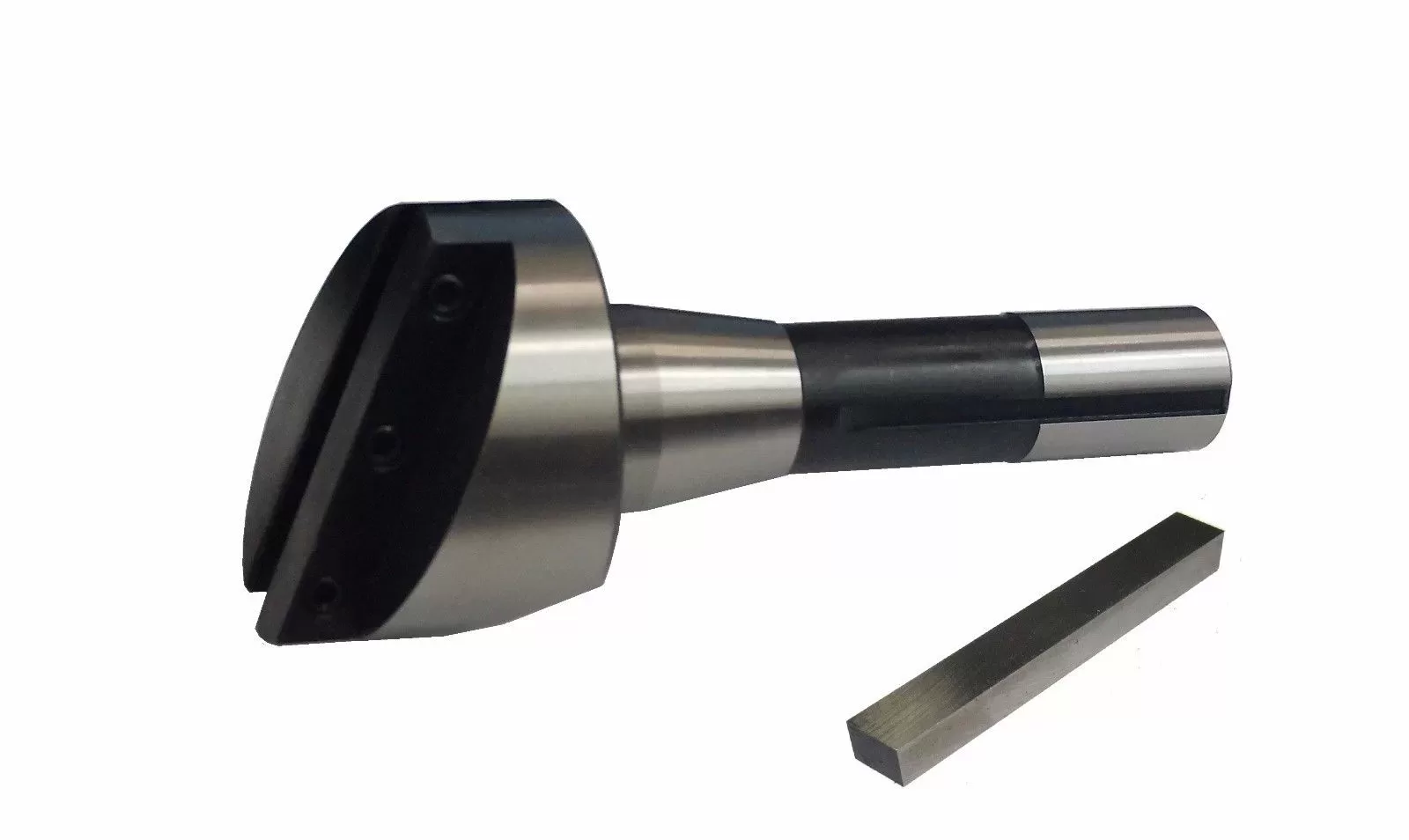

Fly cutters are commonly used for facing operations, where the goal is to create a flat surface on the workpiece. They are especially useful when a large cutting diameter is required. While fly cutters with a single tool bit are more common, those with two tool bits, known as "fly bars," offer a larger cutting diameter and can cover a wider area in a single pass.
Compared to face mills, fly cutters tend to be less expensive, making them a cost-effective option for certain machining applications. They can achieve similar results to face mills, but with a simpler design and fewer parts. The cutting performance and surface finish achieved by a fly cutter may be influenced by factors such as the speed of rotation, feed rate, and the sharpness of the tool bits.
Fly cutters are typically used in milling machines or machining centers. They are well-suited for machining softer materials or when a smooth surface finish is desired. However, they may not be as efficient for high-speed material removal as other cutting tools, such as face mills.
It's important to note that fly cutters require careful setup and adjustment to ensure even cutting across the workpiece surface. Proper tool bit alignment and adjustment of the cutting depth are critical to achieving desired results.
In summary, fly cutters are cutting tools used for facing operations to create flat surfaces on workpieces. They consist of a solid body that holds one or two tool bits, allowing for broad and shallow cuts. While they may not be as versatile or efficient as face mills, fly cutters offer a cost-effective solution for achieving smooth surface finishes in certain machining applications.
5、Thread mill
A thread mill is a cutting tool used to create threads on a workpiece using a CNC machine. While taps are commonly used for threading operations, thread mills offer an alternative method for machining both internal and external threads.
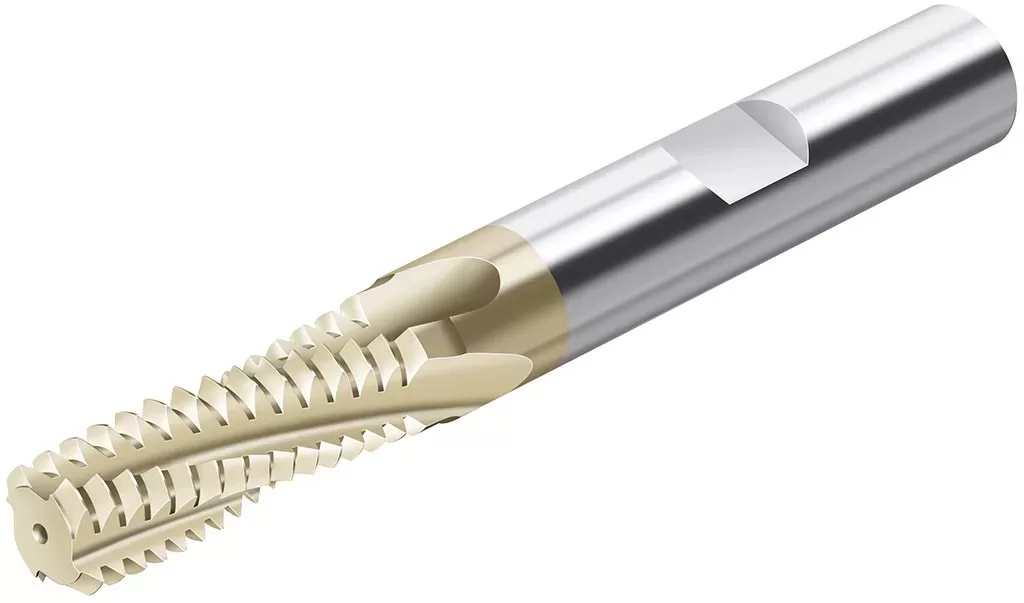

Thread mills are particularly useful in situations where tapping may be challenging or less effective. This includes working with very hard metals or materials that have asymmetrical or difficult-to-machine features.
When using a thread mill, the cutting tool follows a helical path to gradually remove material and create the desired thread profile. The thread mill can be programmed to cut threads with various pitches, sizes, and thread forms, providing flexibility in thread creation.
One advantage of using a thread mill is its ability to penetrate hard metals more effectively compared to taps. The cutting action of the thread mill distributes the cutting forces over multiple teeth, reducing the likelihood of tool breakage or damage. This is especially beneficial when working with materials that are prone to work hardening or have high tensile strength.
Additionally, thread mills can be used for both internal and external threads, making them versatile for a range of applications. By using a CNC machine, precise control over the cutting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut can be achieved, resulting in accurate and consistent threads.
It's worth noting that thread milling typically requires a slower cutting speed compared to tapping. The process may take longer but can offer advantages in terms of tool life and thread quality, especially when dealing with challenging materials or complex workpiece geometries.
In summary, thread mills are cutting tools used in CNC machining for creating threads on workpieces. They offer an alternative to taps and can be particularly beneficial in scenarios involving hard metals or asymmetrical parts. By providing excellent penetration capabilities and the ability to machine both internal and external threads, thread mills offer versatility and precision in thread creation.
6、Drill bit
A drill bit is a cutting tool used in CNC machining to create holes in a workpiece. It typically consists of a fluted body with a conical cutting point at the tip. The flutes or channels in the drill bit help to remove chips and facilitate the cutting process.
In CNC machining, various types of drill bits can be used, depending on the specific application and requirements. Here are a few commonly used drill bits in CNC machining:
- Twist Drill: Twist drills are the most common type of drill bits used in CNC machining. They have a spiral flute design that helps in chip removal. Twist drills are available in various diameters and lengths, allowing for versatility in hole size and depth.
- Center Drill: Center drills, also known as spotting drills, are used to create precise starter holes or centering holes before drilling. They have a short, stiff body with a conical point that helps accurately locate the center of the hole. Center drills are commonly used when drilling holes that require high positional accuracy or when starting a hole on a curved or angled surface.
- Ejector Drill: Ejector drills, also called deep hole drills or gun drills, are specialized drill bits used for deep hole drilling. They feature a long, slender design with internal channels for coolant or chip evacuation. Ejector drills are capable of drilling deep holes with high accuracy and efficiency.
The selection of the appropriate drill bit depends on factors such as the material being drilled, hole size and depth, surface finish requirements, and the specific CNC machining operation. It is important to choose a drill bit with the proper geometry, coating, and cutting parameters to ensure optimal performance and hole quality.
Drill bits are typically made from high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide. Carbide drill bits are known for their durability and ability to withstand high cutting speeds and temperatures. They are commonly used for machining hard materials or for applications that require extended tool life.
In CNC machining, drill bits are mounted in the spindle of the machine, and the workpiece is moved in multiple axes to position the hole accurately. The cutting parameters, such as cutting speed, feed rate, and pecking depth, are carefully controlled to achieve the desired hole dimensions and surface finish.
In summary, drill bits are essential cutting tools in CNC machining for creating holes in workpieces. Twist drills, center drills, and ejector drills are commonly used in various applications. The selection of the appropriate drill bit depends on the specific requirements of the machining operation, including material, hole size, depth, and positional accuracy. By choosing the right drill bit and optimizing cutting parameters, accurate and high-quality holes can be achieved in CNC machining processes.
7、Reamer
A reamer is a cutting tool used in machining operations to enlarge existing holes in a workpiece. It is designed to improve the accuracy, surface finish, and dimensional tolerance of the hole. Reamers typically have multiple flutes and cutting edges, which remove a small amount of material with each pass.
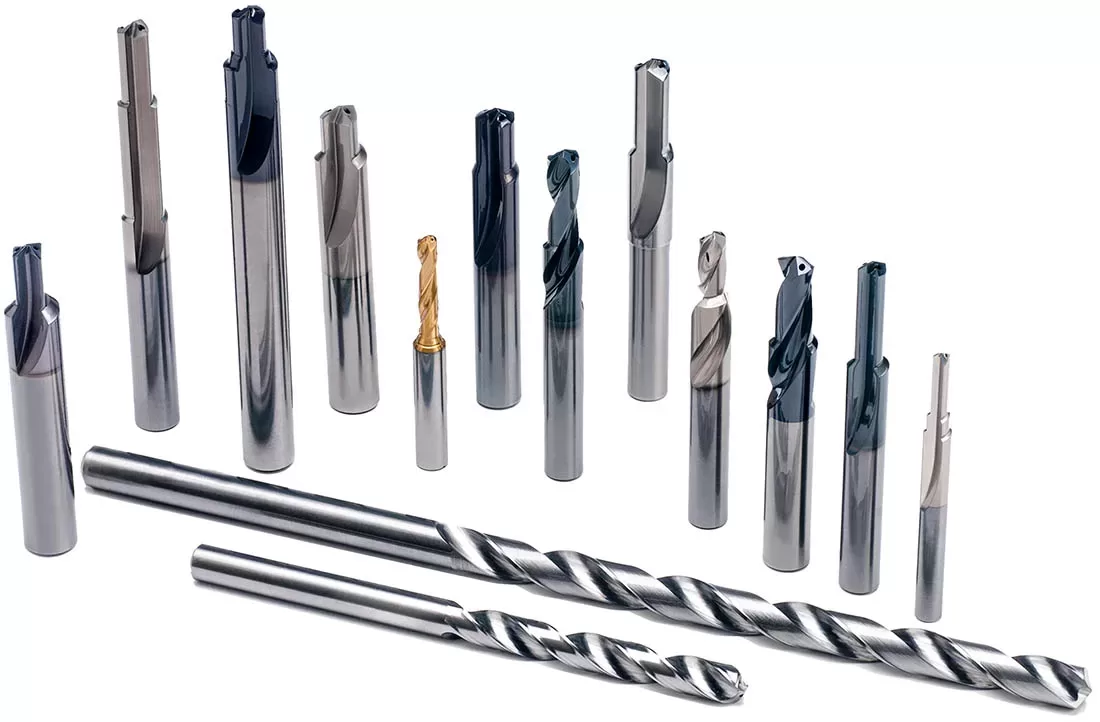

The primary function of a reamer is to ensure that a previously drilled or bored hole achieves the desired diameter and dimensional accuracy. Reamers are commonly used when the hole needs to meet specific tolerances or when a smoother surface finish is required.
Compared to other cutting tools like drills, reamers can achieve much tighter tolerances. They are capable of producing holes with precise diameters, often within a few thousandths of an inch or even less. Reamers allow for fine adjustments to hole size and can create holes with a high degree of roundness and concentricity.
The cutting action of a reamer is different from that of a drill bit. While a drill removes material by cutting and lifting chips, a reamer removes material by shearing and shaving it off. This results in a smoother, more accurate hole surface with reduced burrs and improved finish.
Reamers come in various types, including straight-flute reamers, spiral-flute reamers, and helical-flute reamers. The choice of reamer type depends on factors such as the material being machined, the size and depth of the hole, and the desired surface finish.
When using a reamer, it is important to consider factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and coolant application to optimize the machining process. Proper setup and alignment of the reamer in the machine spindle are also crucial to ensure accurate and concentric hole enlargement.
Reamers are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, precision engineering, and metalworking. They find applications in various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
In summary, reamers are cutting tools used to enlarge existing holes in a workpiece with precision and improved surface finish. They offer the ability to achieve tighter tolerances compared to other cutting tools. Reamers play a critical role in achieving accurate hole dimensions and ensuring high-quality results in machining operations.
8、Hollow mill
A hollow mill cutter, also known as a shell mill or shell end mill, is a cutting tool used in machining operations to create various shapes, such as full points and form radii. It consists of a cylindrical body with cutting edges on the inside or outside periphery. The cutting edges are typically arranged in a helical pattern and can vary in shape depending on the desired cutting profile.
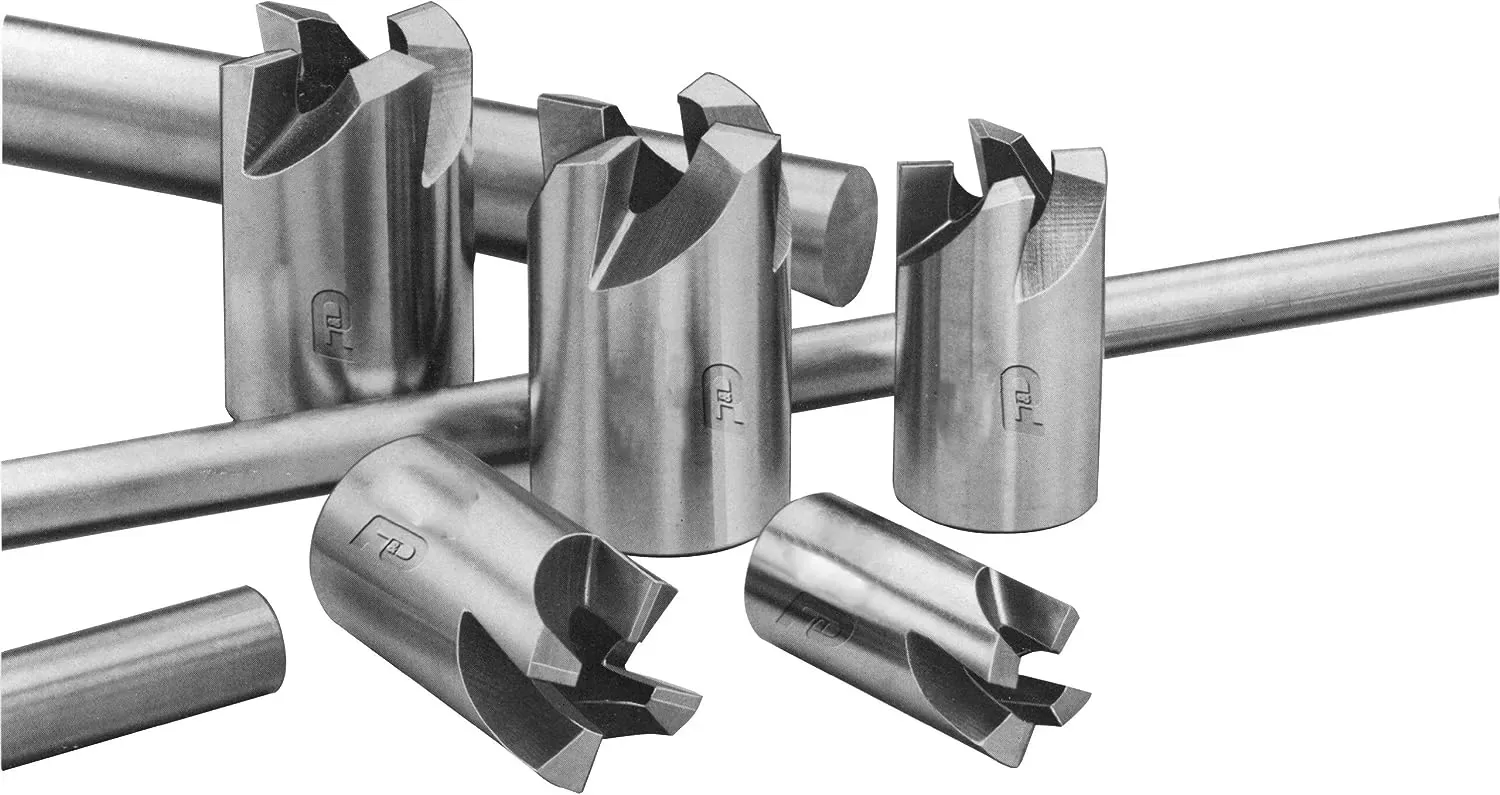
Hollow mill cutters are often used in milling machines and machining centers to perform various operations, including contouring, profiling, and slotting. They are capable of removing material from the workpiece in circular or helical paths, allowing for the creation of intricate shapes and profiles.
The cutting edges of a hollow mill cutter can be sharpened or replaced, providing the flexibility to achieve different cutting profiles and prolonging the tool's lifespan. These cutters are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different machining requirements.
It's important to note that the specific application and usage of a hollow mill cutter may vary depending on the industry and machining context. Therefore, it is recommended to consult industry-specific references or experts for more precise information regarding the hollow mill cutter's applications and capabilities within a particular field.
In summary, a hollow mill cutter, also known as a shell mill or shell end mill, is a cutting tool used in machining operations to create various shapes, including full points and form radii. It features a cylindrical body with cutting edges on the inside or outside periphery, making it suitable for contouring, profiling, and slotting operations.
9、Side-and-face cutter
A side-and-face cutter is a type of milling cutter used in machining operations to perform various cutting tasks, including slotting, grooving, and facing. It is characterized by having cutting teeth on both the side and periphery of the cutter.
The teeth on the side of the cutter are typically used for making side cuts or performing contouring operations, while the teeth on the circumference are used for facing or peripheral cuts. This design allows the side-and-face cutter to remove material simultaneously from the side and the face of the workpiece, making it suitable for performing unbalanced cuts and achieving efficient material removal.
Side-and-face cutters are commonly used in milling machines and machining centers. They are versatile tools that can be employed for a wide range of applications, including creating slots, keyways, grooves, and other complex features. The ability to perform both side and face cuts in a single operation makes them efficient for machining operations that require fast feed rates and increased productivity.
These cutters can have straight teeth or staggered teeth. Straight-tooth side-and-face cutters have cutting edges aligned in a straight manner, while staggered-tooth cutters have cutting edges positioned in a staggered pattern. The choice between straight and staggered teeth depends on the specific machining requirements and the desired surface finish.
Side-and-face cutters are available in various sizes, diameters, and tooth configurations to accommodate different machining needs. The selection of the appropriate cutter depends on factors such as the material being machined, the depth and width of the cut, and the desired machining outcome.
It's important to consider the cutting parameters, such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut, when using side-and-face cutters to ensure optimal performance and achieve the desired results.
In summary, side-and-face cutters are milling cutters with cutting teeth on both the side and periphery of the tool. They are versatile tools used for slotting, grooving, facing, and other machining operations. The ability to perform unbalanced cuts and the availability of different tooth configurations make them suitable for various applications. By selecting the appropriate side-and-face cutter and optimizing cutting parameters, efficient material removal and high-quality machining results can be achieved.
10、Gear cutter
A gear cutter is a specialized cutting tool used in the manufacturing industry to create gears. Gears are essential components used in various mechanical systems to transmit motion and power between rotating shafts.
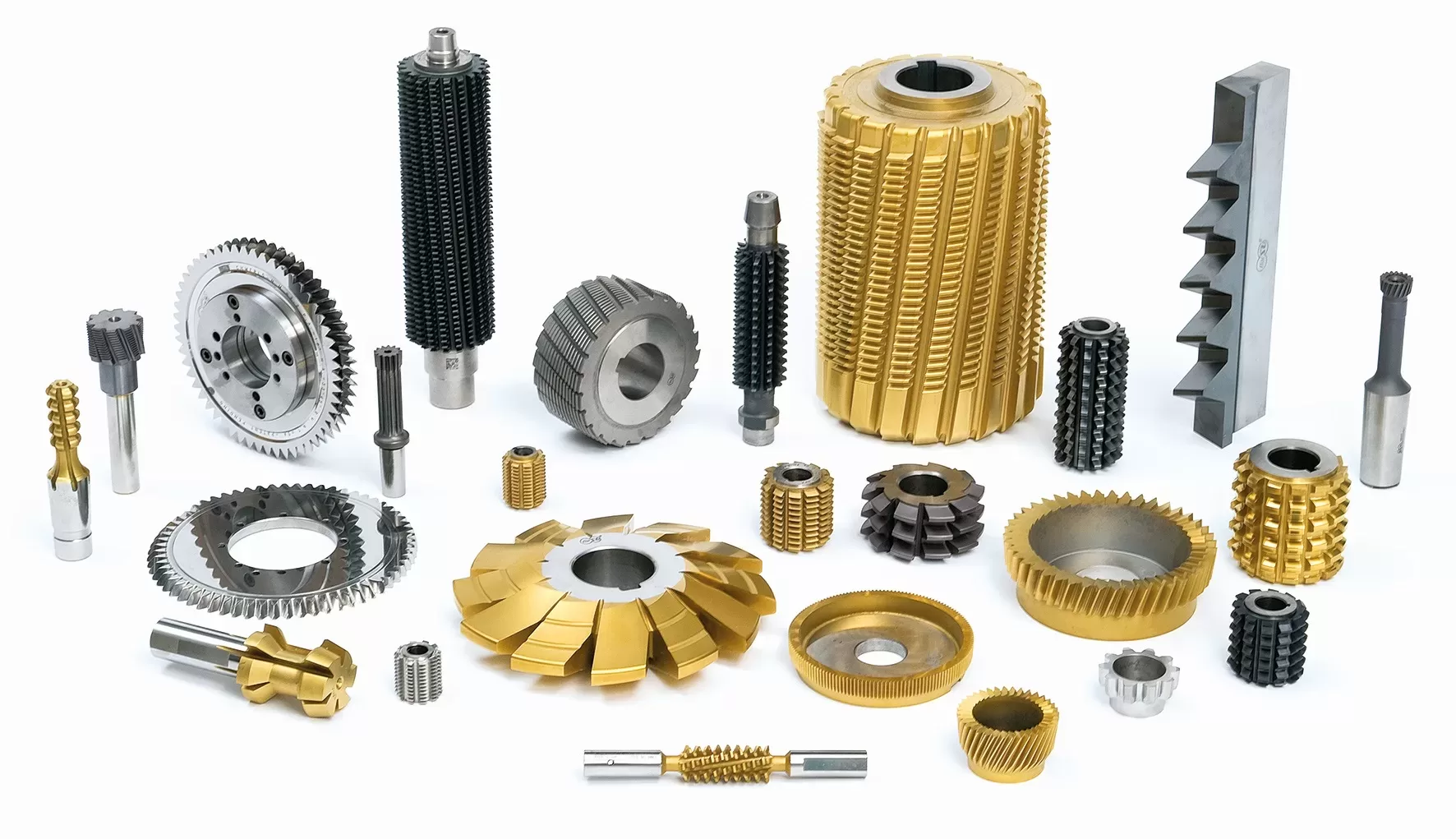

In the context of CNC milling, gear cutters are used to produce metal gears with precise tooth profiles and dimensions. These cutters are designed to accurately shape the teeth of the gear, ensuring proper meshing and smooth operation.
Gear cutters are available in different types, depending on the specific gear profile and the desired cutting method. Here are a few common types of gear cutters:
- Involute Gear Cutter: Involute gear cutters are widely used for cutting spur gears, which have straight teeth parallel to the gear axis. These cutters have the shape of a circular disc with equally spaced cutting teeth along the periphery. They are designed to generate teeth with the involute profile, which is a common tooth form used in many gear applications.
- Hob: A hob is a specialized gear cutter used for generating gears through a process called hobbing. Hobbing is typically performed on a dedicated machine known as a hobbing machine. The hobbing process involves rotating the hob and the workpiece in synchronized motions, resulting in the gradual formation of gear teeth. Hobs are versatile tools that can be used to cut various types of gears, including spur gears, helical gears, and worm gears.
- Gear Shaper Cutter: Gear shaper cutters are used in gear shaping machines to create gears with complex profiles, such as internal gears and gears with irregular tooth forms. These cutters have a unique shape that matches the desired gear profile and are used in a reciprocating motion to shape the gear teeth.
The choice of gear cutter depends on factors such as the gear type, tooth profile, module (pitch), and the required accuracy of the gear. CNC milling machines can be used to produce gears using gear cutters, but for more specialized gear cutting processes like hobbing, dedicated hobbing machines are often employed to achieve high precision and productivity.
It's worth noting that gear cutting is a complex process that requires precise calculations, tool selection, and setup. Depending on the complexity of the gear and the production requirements, gear cutting may involve multiple setup steps, such as indexing the workpiece, adjusting machine parameters, and tool changes.
In summary, gear cutters are specialized cutting tools used in the manufacturing industry to create gears. They come in various types, including involute gear cutters, hobs, and gear shaper cutters. Gear cutters are used in CNC milling machines to produce gears with accurate tooth profiles, while specific gear cutting processes like hobbing require dedicated machines. Gear cutting is a precise and intricate process that plays a crucial role in the production of gears for various mechanical systems.
11、Slab mill
A slab mill, also known as a plain milling cutter or slab cutter, is a type of milling cutter used for machining flat surfaces. It is primarily designed for milling operations where the target surface is mounted parallel to the machine table.
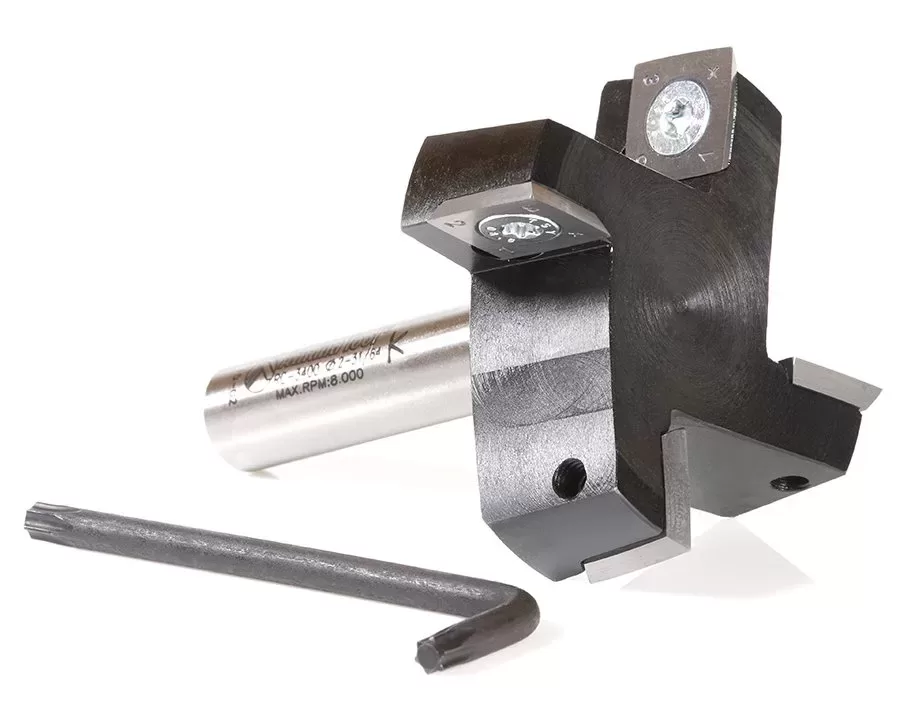

Slab mills are characterized by their cylindrical shape and flat bottom surface. Unlike some other milling cutters, slab mills do not have side teeth. Instead, they feature cutting teeth on the periphery or end of the cutter. The absence of side teeth allows for efficient material removal and smoother cutting action when milling flat surfaces.
These cutting tools are versatile and can be used for a wide range of general or heavy-duty machining operations. They are commonly employed for tasks such as face milling, surface milling, and slotting. Slab mills are particularly useful for removing large amounts of material quickly, making them suitable for roughing operations.
Slab mills are available in various diameters, lengths, and configurations to suit different machining requirements. The choice of cutter size depends on factors such as the size of the workpiece, the desired surface finish, and the required material removal rate.
When using a slab mill, it is important to consider factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut to ensure optimal performance and prolong tool life. Proper fixturing and workpiece clamping are also crucial to ensure stability and accuracy during the milling process.
In summary, a slab mill or plain milling cutter is a cylindrical cutting tool used for milling flat surfaces mounted parallel to the machine table. It does not have side teeth but features cutting teeth on the periphery or end of the cutter. Slab mills are versatile and can be used for general or heavy-duty machining operations, including face milling and surface milling. They are efficient tools for removing large amounts of material quickly and are commonly employed in various industries for milling flat surfaces.
Contact V1 for your metal fabrication needs.
V1 provides professional CNC machining services for your prototyping and production needs.




