- Why is material selection important in injection molding?
- What are the most frequently used materials in injection molding?
-
Which thermoplastics are frequently utilized in injection molding?
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- PP(Polypropylene )
- PE (Polyethylene).
- PC (Polycarbonate)
- PA (Nylon/Polyamide)
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
- PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate)
- PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
- HIPS (High-Impact Polystyrene)
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
- PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate)
- POM (Polyoxymethylene/Acetal)
- PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide)
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- What elastomers are commonly used in injection molding?
- What other materials are commonly used in injection molding?
- What other factors should you consider when choosing a material for injection molding?
When producing parts with injection molding, understanding the range of materials that are available is crucial. Find out more about those materials, their properties, and factors to consider when choosing a material for injection molded parts.
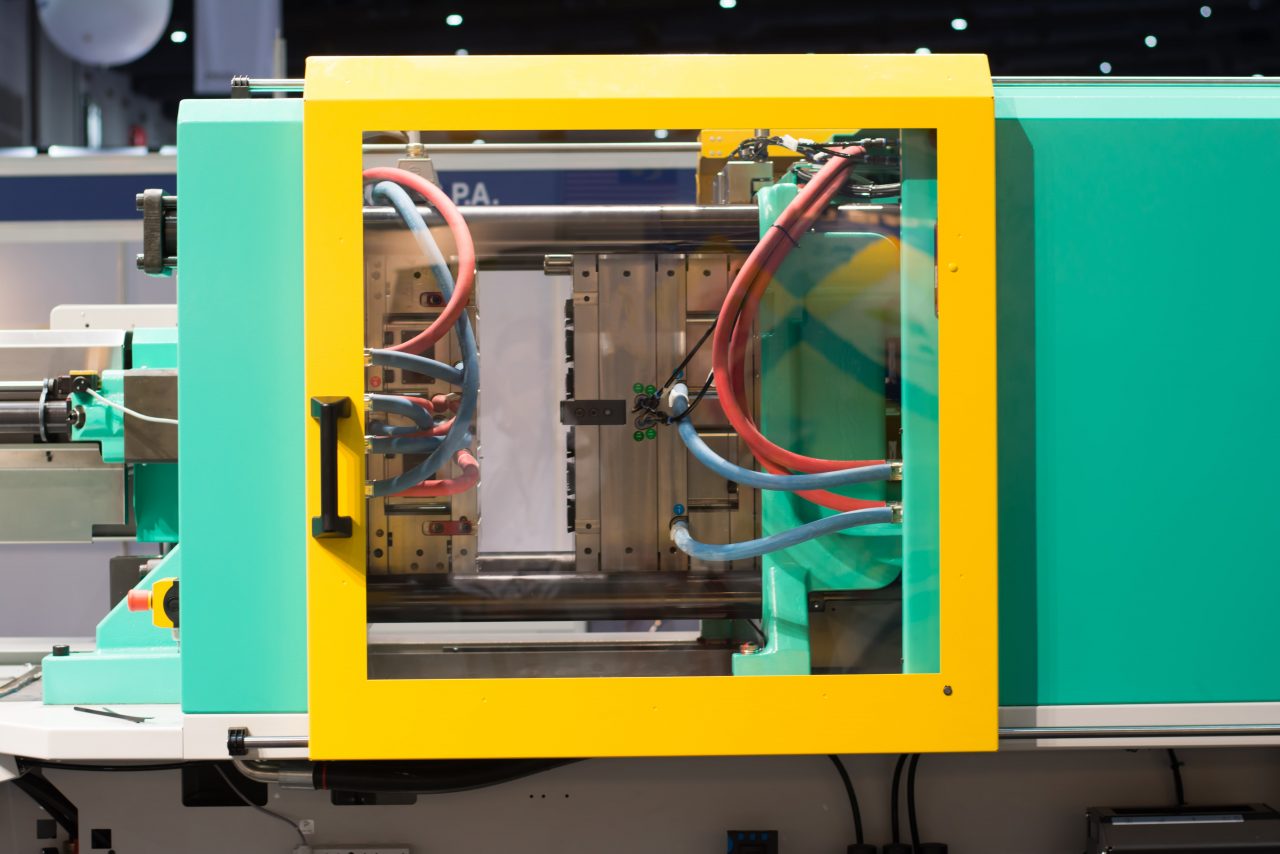
Why is material selection important in injection molding? #
This manufacturing process is widely used to produce complex and high-volume products, but the chosen material will determine the effectiveness of your part. In this article, we explore the material selection process for injection molding and highlight common materials used in this process.
The plastic selected for injection molding will have a significant impact on the quality, performance, and cost of the part. Your material must exhibit properties suitable for the specific application, including mechanical strength, durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
Also, take into account factors such as melt flow characteristics, shrinkage, and warping tendencies to guarantee successful molding processes. The choice of material also impacts processing ease, cycle time, tooling needs, and general production efficiency.
What are the most frequently used materials in injection molding? #
Injection moulding predominantly employs thermoplastics, elastomers, and plastic coatings. Each class of material offers distinct properties, making them suitable for different applications. In the ensuing sections, we will delve into the most usual materials from each of these categories. V1 provides all the materials listed below and can also acquire additional materials upon request.
Which thermoplastics are frequently utilized in injection molding? #
Thermoplastics are preferred for injection moulding due to their capability of being melted, cooled, and solidified numerous times without noteworthy degradation. This enables effective and cost-efficient manufacturing of intricate forms while also fostering recycling and reusability.
Here are some of the most commonly employed thermoplastics for injection molding.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) #
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a popular thermoplastic known for its various desirable properties. Here are some key characteristics and applications of ABS:

- Impact resistance: ABS has excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for applications that require durability and toughness. It can withstand significant loads and absorb energy without fracturing easily.
- Electrical insulation properties: ABS is a good electrical insulator, meaning it does not easily conduct electricity. This property makes it useful in applications where electrical components or insulation are required.
- Low-temperature resistance: ABS retains its mechanical properties even at low temperatures, making it suitable for applications in cold environments. It remains tough and does not become brittle, unlike some other plastics.
- Lightweight: ABS is relatively lightweight compared to many other thermoplastics, making it useful in applications where weight reduction is desired.
- Wide range of applications: ABS is utilized in various industries and sectors due to its versatile properties. Some common applications include automotive parts (e.g., interior trim, dashboards, and bumpers), toys, electronic housings, luggage, pipes, and fittings.
- Injection molding: ABS is particularly well-suited for injection molding processes. It can be easily melted and molded into complex shapes, allowing for efficient and cost-effective mass production. Its popularity in injection molding is also due to its affordability, especially when no additives are used.
It's important to note that while ABS has many advantages, it also has a few limitations. For instance, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications due to its relatively low melting point, and it can be prone to degradation when exposed to certain chemicals or UV radiation over time. However, with proper design considerations and material selection, ABS can be a highly useful thermoplastic for a wide range of applications.
PP(Polypropylene ) #
Polypropylene (PP) is indeed a lightweight thermoplastic with several advantageous properties. Here's some more information about PP:

Properties of PP:
- Lightweight: PP is a lightweight material, which makes it suitable for applications where weight reduction is desired, such as in packaging or automotive components.
- Moisture resistance: PP has excellent moisture resistance, meaning it does not absorb water easily. This property makes it ideal for applications where exposure to moisture or water is a concern.
- Chemical resistance: PP exhibits good chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand a wide range of chemicals, acids, and bases. This property makes it suitable for applications in the chemical industry, as well as for containers or pipes that may come into contact with various substances.
- Low-temperature resistance: PP performs well at low temperatures and remains tough and flexible even in cold environments. This property makes it suitable for applications in freezer storage, cold weather conditions, or other low-temperature environments.
- Cost-effective and injection molding: PP is known for its cost-effectiveness, making it an economical choice for many applications. It can be efficiently processed through injection molding, enabling mass production of parts with complex geometries at a relatively low cost.
Applications of PP:
- Packaging: PP is widely used in packaging applications, such as food containers, bottles, caps, and films. Its moisture resistance and durability make it suitable for protecting and preserving various products.
- Toys: PP's lightweight and impact-resistant properties make it popular for the production of toys, including molded toys, building blocks, and outdoor play equipment.
- Household items: PP is commonly used in the manufacturing of household items like storage containers, kitchenware, furniture, and appliances due to its moisture resistance, durability, and affordability.
- Automotive components: PP is also utilized in automotive applications, including interior trims, bumpers, dashboards, and battery cases, where its low weight, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness are advantageous.
It's worth noting that while PP has many beneficial properties, it has a relatively low heat resistance compared to some other thermoplastics. Therefore, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications where other materials like ABS or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) might be preferred
PE (Polyethylene). #
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic with various advantageous properties. Here's some more information about PE:

Properties of PE:
- Lightweight: PE is a lightweight material, which makes it suitable for applications where weight reduction is desired, such as in packaging or products that require portability.
- Moisture resistance: PE exhibits excellent moisture resistance, meaning it does not readily absorb water. This property makes it ideal for applications where exposure to moisture or water is a concern, such as in packaging for food or beverages.
- Good electrical insulation: PE is an effective electrical insulator, meaning it does not easily conduct electricity. This property makes it suitable for applications where electrical insulation is required, such as in wire and cable coatings or electrical components.
- Low-temperature resistance: PE performs well at low temperatures and retains its flexibility and impact resistance even in cold environments. This property makes it suitable for applications in freezer storage, cold weather conditions, or other low-temperature environments.
- Cost-effective and ease of processing: PE is known for being a cost-effective material, making it widely used in various industries. It is relatively easy to process through injection molding, extrusion, or blow molding processes, enabling efficient and economical production.
Applications of PE:
- Packaging: PE is extensively used in packaging applications due to its moisture resistance and durability. It is commonly used for plastic bags, films, containers, bottles, and other packaging materials.
- Toys: PE's lightweight and impact-resistant properties make it suitable for the production of toys, including molded toys, playground equipment, and inflatable structures.
- Household items: PE is used in the manufacturing of various household items such as storage containers, buckets, trash cans, and household appliances due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.
- Pipes and fittings: PE is widely used in the construction industry for pipes and fittings due to its excellent chemical resistance, low-temperature performance, and durability.
- Agricultural applications: PE is also used in agricultural applications, such as irrigation pipes, greenhouse films, and agricultural films, owing to its resistance to moisture and chemicals.
It's important to note that there are different types of polyethylene, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), each with slightly different properties and applications.
PC (Polycarbonate) #
Polycarbonate (PC) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its exceptional properties. Here's some more information about PC:

Properties of PC:
- High impact strength: PC is renowned for its high impact resistance, making it highly durable and able to withstand significant forces or impacts without breaking or shattering easily. This property makes it suitable for applications where safety and durability are crucial.
- Transparency: PC is a transparent material with excellent optical clarity, allowing for the transmission of light. This property makes it suitable for applications where transparency or visibility is desired, such as in safety glasses or windows.
- Heat resistance: PC exhibits good heat resistance, allowing it to withstand elevated temperatures without significant deformation or degradation. It can typically withstand temperatures higher than other common thermoplastics, making it suitable for applications where heat resistance is essential.
- Electrical insulation: PC is an excellent electrical insulator, meaning it has high electrical resistance and does not easily conduct electricity. This property makes it suitable for applications involving electrical components or insulation.
- Dimensional stability: PC has good dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size even under varying temperature conditions. This property makes it suitable for applications where consistent dimensions are crucial, such as precision components or optical lenses.
Applications of PC:
- Electronic components: PC is widely used in the electronics industry for various applications, including electrical housings, connectors, sockets, and LED light diffusers, due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and dimensional stability.
- Safety glasses and face shields: PC's high impact strength and transparency make it an ideal material for safety glasses, goggles, face shields, and other protective equipment. Its ability to withstand impact while maintaining visibility is crucial for ensuring eye and face protection.
- Automotive applications: PC is used in automotive applications such as headlamp lenses, interior trim components, instrument panels, and sunroof panels due to its impact resistance, heat resistance, and transparency.
- Medical devices: PC is utilized in the medical industry for applications like medical device housings, surgical instrument components, transparent tubing, and IV connectors, where its transparency, impact resistance, and sterilization compatibility are advantageous.
- Optical applications: PC's optical clarity and impact resistance make it suitable for optical applications such as lenses for eyewear, camera lenses, and displays.
Due to its exceptional properties, PC is generally considered a higher-cost material compared to some other thermoplastics. However, its unique combination of properties often justifies its use in applications where its benefits outweigh the cost considerations.
PA (Nylon/Polyamide) #
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon and abbreviated as PA, is a strong and versatile thermoplastic with several desirable properties. Here's some more information about PA:

Properties of PA:
- Strength and wear resistance: PA exhibits high tensile strength and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring mechanical strength and durability. It can withstand heavy loads and repetitive stress without significant deformation.
- Fatigue resistance: PA has good fatigue resistance, meaning it can endure repeated loading and unloading cycles without experiencing failure or degradation. This property makes it suitable for applications subjected to cyclic stress or vibration, such as gears or mechanical parts.
- Heat resistance: PA possesses good heat resistance compared to many other thermoplastics. It can withstand moderately high temperatures without significant deformation or loss of mechanical properties. This property makes it suitable for applications where heat resistance is required, such as in engine components or under-the-hood parts.
- Chemical resistance: PA exhibits good chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand exposure to various chemicals, oils, and solvents. This property makes it suitable for applications where resistance to chemical substances is essential.
Applications of PA:
- Mechanical parts: PA is widely used in the manufacturing of mechanical parts, such as bearings, gears, bushings, and structural components. Its combination of strength, wear resistance, and fatigue resistance makes it suitable for demanding mechanical applications.
- Electrical components: PA is used in electrical and electronic applications, including connectors, switches, cable ties, and insulating parts. Its electrical insulation properties, combined with its mechanical strength, make it suitable for such applications.
- Automotive industry: PA finds applications in the automotive industry, including under-the-hood components, fuel system parts, engine covers, and interior trim components. Its strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance make it suitable for these demanding environments.
- Consumer goods: PA is used in various consumer goods, such as sports equipment, tools, zippers, and fasteners, due to its strength, durability, and wear resistance.
- Textiles: PA is also used in the textile industry for applications such as nylon fibers, fabrics, and ropes due to its high strength and abrasion resistance.
Due to its superior properties and performance, PA is generally considered a higher-cost material compared to some other thermoplastics. However, its exceptional strength, wear resistance, and heat resistance often justify its use in applications where its benefits outweigh the cost considerations.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) #
A lightweight thermoplastic with excellent moisture resistance and good chemical resistance. It also offers low-temperature resistance. However, it is not as strong as materials such as ABS or PC, and is prone to warping and shrinking during the injection molding process. HDPE finds applications in packaging, toys, and household items. It tends to be high in cost.

Let's go through the details about High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
Properties of HDPE:
- Lightweight: HDPE is a lightweight thermoplastic, which makes it suitable for applications where weight reduction is desired without sacrificing strength or durability.
- Excellent moisture resistance: HDPE exhibits excellent moisture resistance and does not readily absorb water. This property makes it suitable for applications where exposure to moisture or water is a concern, such as in packaging or outdoor applications.
- Good chemical resistance: HDPE has good chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand a wide range of chemicals, acids, and bases. This property makes it suitable for applications in the chemical industry, as well as for containers or pipes that may come into contact with various substances.
- Low-temperature resistance: HDPE performs well at low temperatures and remains tough and flexible even in cold environments. This property makes it suitable for applications in freezer storage, cold weather conditions, or other low-temperature environments.
Regarding the comparison to other materials:
- Strength: While HDPE may not have the same strength as materials like ABS or PC, it still possesses good strength and impact resistance for many applications. It is known for its toughness and durability.
- Warping and shrinking during injection molding: HDPE generally has low shrinkage and is less prone to warping compared to some other thermoplastics. It can be effectively injection molded with proper processing techniques and design considerations.
Applications of HDPE:
- Packaging: HDPE is widely used in packaging applications, such as bottles, containers, jugs, and bags. Its moisture resistance, durability, and versatility make it suitable for a wide range of packaging needs.
- Toys: HDPE's lightweight and impact-resistant properties make it suitable for the production of toys, including molded toys, building blocks, and outdoor play equipment.
- Household items: HDPE is commonly used in the manufacturing of household items like storage containers, buckets, trash cans, and various household appliances due to its moisture resistance, durability, and ease of cleaning.
- Pipes and fittings: HDPE is widely used in the construction industry for pipes, fittings, and drainage systems due to its excellent chemical resistance, low-temperature performance, and durability.
Regarding the cost, HDPE is generally considered a cost-effective material compared to some other thermoplastics. Its availability and ease of processing contribute to its affordability. However, pricing can vary based on factors such as grade, quantity, and specific application requirements.
It's important to note that HDPE is available in different grades and variations, each with slightly different properties and suitability for specific applications.
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) #
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or acrylic glass, is a transparent thermoplastic with several notable properties. Let's delve into the details:

Properties of PMMA:
- Transparency and optical clarity: PMMA is known for its excellent transparency, allowing for high light transmission. It has optical properties similar to glass, providing good clarity and minimizing distortion.
- Weather resistance: PMMA exhibits good weather resistance, enabling it to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight, UV radiation, and outdoor elements without significant degradation or yellowing. This property makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
- Moldability and dimensional stability: PMMA can be easily molded into complex shapes due to its excellent melt flow characteristics. It maintains good dimensional stability, retaining its shape and size even under varying temperature conditions.
- Scratch and impact resistance: PMMA has moderate scratch resistance, but it is not as resistant to scratching as materials like polycarbonate. It is more prone to surface scratches, which can affect its appearance over time. However, it offers good impact resistance compared to glass.
- Chemical sensitivity: PMMA is sensitive to certain chemicals, solvents, and cleaning agents. Exposure to harsh chemicals can cause cracking or crazing of the material. Additionally, PMMA has a lower heat resistance compared to some other thermoplastics, and exposure to high temperatures can lead to deformation or melting.
Applications of PMMA:
- Automotive parts: PMMA is used in automotive applications like light covers, indicators, tail lights, and interior trim components due to its optical clarity, weather resistance, and ease of molding.
- Lighting fixtures: PMMA is widely used in the production of light fixtures, including light diffusers, lenses, and covers. Its optical clarity and light transmission properties make it suitable for efficient light distribution.
- Displays and signage: PMMA is commonly used in displays, POS (point of sale) materials, signage, and exhibition stands. Its transparency, dimensional stability, and ease of fabrication allow for attractive and eye-catching designs.
- Protective barriers: PMMA is used in protective barriers, such as sneeze guards, safety screens, and barriers in public spaces. Its impact resistance and transparency make it suitable for maintaining visibility while providing protection.
- Medical devices: PMMA finds applications in certain medical devices, such as dental prosthetics, orthopedic implants, and intraocular lenses, due to its biocompatibility and optical properties.
PMMA falls within the moderate cost range compared to some other high-performance plastics. The pricing can vary based on factors such as sheet thickness, size, and specific requirements for optical quality.
It's worth noting that PMMA is available in various grades, including standard, impact-modified, and UV-resistant grades, each with specific properties suitable for different applications.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) #
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is indeed a high-performance thermoplastic with exceptional properties. Let's explore them in more detail:

Properties of PEEK:
- High temperature resistance: PEEK exhibits excellent heat resistance, allowing it to withstand continuous use at high temperatures up to around 250-300°C (482-572°F). It retains its mechanical properties and dimensional stability even at elevated temperatures.
- Chemical resistance: PEEK is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, solvents, and hydrocarbons. It can withstand aggressive chemical environments and is often used in applications where chemical resistance is crucial.
- Mechanical strength: PEEK possesses high mechanical strength and rigidity, making it suitable for demanding applications that require structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities. It has a high tensile strength and can withstand high stress and impact.
- Electrical insulation properties: PEEK is an excellent electrical insulator, with high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in electrical and electronic applications where electrical insulation and performance are critical.
- Dimensional stability: PEEK exhibits low creep and excellent dimensional stability, maintaining its shape and size even under prolonged stress or varying temperature conditions. This property is important for applications requiring precise tolerances and consistent performance.
Applications of PEEK:
- Aerospace industry: PEEK is widely used in the aerospace industry for various applications, including aircraft components, engine parts, seals, bushings, and electrical connectors. Its high temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance make it suitable for harsh aerospace environments.
- Medical devices: PEEK is utilized in the medical field for applications such as orthopedic implants, dental implants, surgical instruments, and medical equipment components. Its biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and sterilizability make it a preferred material in medical applications.
- Electrical and electronics: PEEK finds applications in electrical connectors, insulators, coil bobbins, and other electrical components due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to high temperatures.
- Oil and gas industry: PEEK is used in the oil and gas sector for components like seals, valves, pump parts, and downhole tools. Its chemical resistance and high-temperature performance make it suitable for demanding oil and gas applications.
- Automotive industry: PEEK is employed in automotive applications that require high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Examples include connectors, sensors, fuel system components, and electrical connectors.
PEEK is considered a more expensive material compared to standard thermoplastics like ABS or PP. The exceptional properties of PEEK, such as high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, contribute to its higher cost. However, its performance and reliability in demanding applications often justify the investment.
It's worth noting that PEEK is available in different grades and forms, including unreinforced PEEK, glass fiber-reinforced PEEK, and carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK, each with specific enhancements suited for different applications.
HIPS (High-Impact Polystyrene) #
High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is a versatile thermoplastic with several notable properties. Let's explore them in more detail:

Properties of HIPS:
- Lightweight and rigid: HIPS is a lightweight material that provides rigidity and structural integrity to products. It offers a good balance between strength and weight, making it suitable for applications where both properties are important.
- Dimensional stability: HIPS exhibits good dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size even under varying temperature and humidity conditions. This property is crucial for applications that require precise tolerances and consistent dimensions.
- Impact resistance: HIPS is formulated to have high impact resistance, making it less prone to cracking or breaking when subjected to sudden impacts or stress. This property makes it suitable for applications where durability and toughness are desired.
- Versatility: HIPS is a versatile material that can be easily molded into complex shapes and forms. It can be processed using various techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming, allowing for a wide range of manufacturing possibilities.
Applications of HIPS:
- Packaging: HIPS is commonly used in packaging applications, including food packaging, disposable containers, trays, and blister packs. Its lightweight nature, rigidity, and affordability make it an attractive choice for packaging solutions.
- Toys: HIPS is widely used in the production of toys, including building blocks, action figures, puzzles, and model kits. Its lightweight, impact resistance, and ease of molding into complex shapes make it suitable for toy manufacturing.
- Electrical components: HIPS is utilized in electrical and electronic applications, such as housings for electronic devices, electrical enclosures, switchgear components, and connectors. Its electrical insulation properties, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for these applications.
- Consumer products: HIPS is found in a variety of consumer products, including bathroom accessories, stationery items, kitchenware, and household appliances. Its affordability, lightweight nature, and ease of processing contribute to its widespread use in these applications.
HIPS is generally considered a moderate-cost material compared to some other thermoplastics. Its availability, ease of processing, and versatility contribute to its affordability. The exact pricing can vary based on factors such as grade, quantity, and specific application requirements.
It's important to note that HIPS can be modified by incorporating additives or fillers to enhance specific properties, such as flame resistance, UV resistance, or improved impact strength, depending on the desired application.
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) #
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic material with several notable properties. Let's explore them in more detail:

Properties of LDPE:
- Lightweight and flexible: LDPE is a lightweight material known for its flexibility and elasticity. It offers good elongation properties, allowing it to be easily stretched or bent without breaking. This flexibility makes LDPE suitable for applications that require pliability and impact resistance.
- Chemical resistance: LDPE exhibits good resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. It is less susceptible to chemical attack compared to other thermoplastics, making it suitable for packaging applications where contact with various substances is expected.
- Low-temperature resistance: LDPE performs well in low-temperature environments. It remains flexible and retains its mechanical properties at sub-zero temperatures, which makes it useful in applications that require cold storage, such as freezer bags or medical packaging.
- Moisture resistance: LDPE has good moisture resistance, providing a barrier against water vapor and moisture ingress. This property makes it suitable for applications where moisture protection is required, such as packaging for food and pharmaceutical products.
- Impact resistance: LDPE exhibits good impact resistance, making it less prone to cracking or breaking when subjected to impact or stress. This property is beneficial for applications that require durability and toughness, such as toys or protective packaging.
Applications of LDPE:
- Packaging: LDPE is widely used in packaging applications, including plastic bags, shrink films, stretch films, and pouches. Its flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for various packaging needs.
- Toys and recreational products: LDPE is commonly used in the production of toys, inflatable products, pool floats, and sports equipment. Its flexibility, impact resistance, and ability to be molded into different shapes make it suitable for these applications.
- Household items: LDPE is found in numerous household items such as squeeze bottles, food containers, trash bags, and storage bins. Its flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of processing contribute to its use in everyday household products.
- Agricultural films: LDPE is used in agricultural applications for greenhouse films, mulch films, and crop covers. Its ability to protect crops from moisture, weeds, and pests, combined with its flexibility and durability, makes it suitable for agricultural use.
- Medical and healthcare products: LDPE is utilized in medical and healthcare applications such as disposable gloves, medical packaging, and tubing. Its low-temperature resistance, flexibility, and compatibility with sterilization methods make it suitable for these applications.
LDPE is considered a cost-effective material choice due to its availability, ease of processing, and versatility. Its combination of flexibility, durability, chemical resistance, and low-temperature performance makes it suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries.
PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) #
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic material with several notable properties. Let's explore them in more detail:

Properties of PBT:
- Dimensional stability: PBT exhibits excellent dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size under varying temperature and humidity conditions. This property makes it suitable for applications that require precise tolerances and consistent dimensions.
- Chemical resistance: PBT has good resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including solvents, oils, and fuels. It is less susceptible to chemical attack compared to some other thermoplastics, making it suitable for applications that involve exposure to various substances.
- Impact strength: PBT offers good impact resistance, making it less prone to cracking or breaking under impact or stress. This property makes it suitable for applications where durability and toughness are required.
- Electrical insulation properties: PBT is an excellent electrical insulator, with good dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in electrical and electronic applications that require electrical insulation and performance.
- Heat resistance: PBT exhibits good heat resistance, allowing it to withstand continuous use at elevated temperatures. While not as heat resistant as some other high-performance thermoplastics like PEEK, PBT can still perform well in moderately high-temperature environments.
Applications of PBT:
- Electrical components: PBT is widely used in electrical and electronic applications, such as connectors, sockets, insulators, switches, and circuit breakers. Its electrical insulation properties, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance make it suitable for these applications.
- Automotive parts: PBT finds extensive use in the automotive industry for various components, including connectors, housings, sensors, switches, and engine parts. Its combination of dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and impact strength makes it suitable for the demanding automotive environment.
- Consumer goods: PBT is utilized in the production of consumer goods such as appliance parts, handles, housings for electronic devices, and household items. Its properties, including dimensional stability and impact strength, contribute to its use in these applications.
- Industrial applications: PBT is used in various industrial applications, including machinery components, gears, bearings, and pump parts. Its good dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and impact strength make it suitable for these industrial environments.
PBT is generally considered a moderate-cost material. Its availability, ease of processing, and desirable properties contribute to its cost-effectiveness. The exact pricing can vary based on factors such as grade, quantity, and specific application requirements.
It's important to note that PBT can be modified by incorporating additives or fillers to enhance specific properties, such as flame resistance, UV resistance, or improved impact strength, depending on the desired application.
POM (Polyoxymethylene/Acetal) #
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as Acetal, is a thermoplastic material with several notable properties. Let's explore them in more detail:

Properties of POM:
- Low friction: POM exhibits low friction characteristics, making it suitable for applications where reduced friction and wear are desired. This property allows for smooth movement and sliding between components, reducing energy loss and minimizing the need for lubrication.
- Dimensional stability: POM has excellent dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size under varying temperature and humidity conditions. This property makes it suitable for applications that require precise tolerances and consistent dimensions over time.
- High mechanical strength: POM offers high mechanical strength, including excellent tensile and flexural strength. It has good resistance to deformation and can withstand heavy loads and stresses, making it suitable for applications requiring high strength and rigidity.
- Chemical resistance: POM exhibits good resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including solvents, fuels, and oils. It is less susceptible to chemical attack compared to many other thermoplastics, making it suitable for applications that involve exposure to various substances.
- Excellent machinability: POM is known for its excellent machinability, allowing for precise machining and manufacturing of complex parts. It can be easily turned, milled, drilled, or molded into various shapes and forms, making it suitable for applications with intricate designs.
Applications of POM:
- Mechanical parts: POM is widely used in mechanical engineering applications, including gears, bearings, bushings, rollers, and other precision components. Its low friction, dimensional stability, and high mechanical strength make it ideal for these applications.
- Electrical components: POM is utilized in electrical and electronic applications, such as connectors, switches, insulators, and housings. Its electrical insulation properties, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance make it suitable for these applications.
- Automotive industry: POM finds extensive use in the automotive industry for various components, including fuel system components, door handles, seat belt components, and interior trims. Its combination of low friction, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance make it suitable for demanding automotive applications.
- Consumer goods: POM is used in the production of consumer goods such as zippers, fasteners, handles, and various household items. Its low friction, high strength, and dimensional stability contribute to its use in these applications.
POM is generally considered a high-cost material compared to many other thermoplastics. Its higher cost is due to factors such as the raw material cost, the production process, and its desirable properties. However, the higher cost is often justified by the performance and advantages it offers in specific applications.
It's important to note that POM can be compounded or modified with additives to enhance specific properties, such as improved wear resistance, impact resistance, or flame retardancy, depending on the desired application.
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) #
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional properties. Let's explore them in more detail:

Properties of PPS:
- High temperature resistance: PPS exhibits excellent heat resistance, making it capable of withstanding continuous use at elevated temperatures. It has a high melting point and can maintain its mechanical and dimensional stability even at temperatures above 200°C (392°F). This property makes it suitable for high-temperature applications where other thermoplastics may degrade or lose their properties.
- Chemical resistance: PPS demonstrates excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, solvents, and fuels. It is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand exposure to aggressive environments. This property makes it suitable for applications where chemical resistance is critical.
- Dimensional stability: PPS has outstanding dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape, size, and mechanical properties with minimal shrinkage or expansion under varying temperature and environmental conditions. This property makes it suitable for applications that require precise tolerances and dimensional accuracy.
- Electrical insulation properties: PPS is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity. It exhibits stable electrical properties over a wide temperature range, making it suitable for electrical and electronic applications that require reliable insulation.
- Mechanical strength: PPS offers high mechanical strength and stiffness, allowing it to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation. It has good tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications that require structural integrity and toughness.
Applications of PPS:
- Electrical components: PPS is widely used in electrical and electronic applications, including connectors, sockets, circuit breakers, switches, and insulators. Its high temperature resistance, excellent electrical insulation properties, and chemical resistance make it suitable for these applications.
- Automotive parts: PPS finds extensive use in the automotive industry for various components, including fuel system components, sensors, connectors, and under-the-hood applications. Its combination of high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability makes it suitable for demanding automotive environments.
- Industrial applications: PPS is utilized in various industrial applications, such as pump and valve components, gaskets, seals, and bearings. Its high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength make it suitable for these industrial environments.
PPS is considered a higher-cost material compared to many other thermoplastics due to its exceptional properties and the more complex manufacturing processes involved in its production. The cost is influenced by factors such as raw material costs, processing requirements, and specific application demands. However, the higher cost is often justified by the superior performance and advantages it offers in high-temperature and chemically challenging applications.
It's important to note that PPS can be reinforced with glass fibers or other additives to further enhance its mechanical properties, such as improved strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability, depending on the specific application requirements.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) #
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic material known for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Let's delve into its properties and applications:

Properties of PVC:
- Lightweight: PVC is a lightweight material, which makes it easy to handle and transport. Its low density contributes to its widespread use in various applications where weight reduction is desirable.
- Chemical resistance: PVC exhibits excellent chemical resistance to many acids, bases, salts, and other chemicals. It is less prone to corrosion and degradation compared to some other materials, making it suitable for applications where exposure to various substances is expected.
- Electrical insulation properties: PVC is a good electrical insulator, offering reliable electrical insulation and low electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in electrical cables, wires, and insulation materials where electrical safety and insulation properties are required.
- Durability: PVC is a durable material, capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, impact, and wear. It is resistant to moisture, weathering, and UV radiation, which contributes to its long service life in outdoor applications.
- Cost-effectiveness: PVC is generally a low-cost material compared to many other thermoplastics. Its affordability is due to the abundance of raw materials used in its production and the relatively simple manufacturing processes involved.
Applications of PVC:
- Pipes and fittings: PVC is extensively used in the construction industry for plumbing and drainage systems. PVC pipes offer corrosion resistance, easy installation, and long-term durability, making them suitable for water supply, sewage, irrigation, and other fluid transportation systems.
- Electrical cables and insulation: PVC is widely used as an insulation material for electrical wires and cables. Its excellent electrical insulation properties, combined with cost-effectiveness, make it a popular choice in the electrical and electronics industry.
- Construction materials: PVC is utilized in various construction materials, including window frames, doors, roofing membranes, and flooring. Its durability, weather resistance, and ease of maintenance contribute to its use in these applications.
- Packaging: PVC is used in packaging applications, such as blister packs, clamshells, and shrink wrap films. It provides transparency, protection, and product visibility, making it suitable for packaging various consumer goods.
- Vinyl records and clothing: PVC is a key component in vinyl records due to its excellent sound quality and durability. It is also used in the production of synthetic leather and vinyl clothing items.
PVC's low cost, combined with its desirable properties and wide range of applications, has contributed to its popularity in various industries. However, it's important to note that PVC can release toxic substances when burned, and its disposal requires proper consideration to minimize environmental impact.
What elastomers are commonly used in injection molding? #
When it comes to elastomers commonly used in injection molding, the focus is primarily on thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). Silicone rubber, although not typically processed through traditional injection molding, is worth mentioning as it is commonly used in other manufacturing methods.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs): TPEs are a class of materials that combine the characteristics of rubber and thermoplastics. They can be melted and re-melted multiple times without undergoing significant degradation. TPEs offer excellent flexibility, elasticity, and resilience, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They can be formulated to have different hardness levels, ranging from soft and rubbery to harder and more rigid. TPEs find applications in automotive components, consumer products, medical devices, and more.
- Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): TPU is a versatile elastomer known for its excellent flexibility, resilience, and abrasion resistance. It offers a wide range of hardness options, from very soft to semi-rigid, depending on the application requirements. TPU exhibits good chemical resistance and can withstand harsh environmental conditions. It is commonly used in automotive parts, footwear, industrial components, and consumer goods.
- Silicone Rubber: Although not typically processed through injection molding due to its curing process, silicone rubber is worth mentioning. It is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent temperature resistance, flexibility, and biocompatibility. Silicone rubber finds applications in various industries, including automotive, medical, electronics, and food handling.
Regarding shrinkage and draft angles, elastomers, including TPEs and TPUs, do exhibit shrinkage during the cooling process after injection molding. The specific shrinkage values and draft angle requirements can vary depending on the material, part design, and processing conditions. It is recommended to consult material suppliers and design guidelines specific to the elastomer being used to ensure proper design considerations.
What other materials are commonly used in injection molding? #
Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW) is another material commonly used in injection molding for specific applications. Here are some key points about UHMW:
- Properties: UHMW is known for its exceptionally high molecular weight, which contributes to its unique properties. It offers excellent abrasion resistance, impact strength, and chemical resistance. UHMW has a low coefficient of friction, making it suitable for applications requiring reduced friction and wear.
- Applications: UHMW is commonly used in applications where its specialized properties are beneficial. Some examples include:
- Bearings and Bushings: UHMW's low friction properties make it ideal for use in bearings and bushings, reducing friction and extending the component's lifespan.
- Gears and Sprockets: UHMW's high impact strength and self-lubricating properties make it suitable for gears and sprockets, particularly in applications where noise reduction and smooth operation are desired.
- Conveyor Components: UHMW is used for wear strips, guide rails, and other components in conveyor systems due to its excellent abrasion resistance and low friction characteristics.
- Chute Liners: UHMW is often employed as a liner material in chutes to reduce friction and prevent material build-up.
- Manufacturing Considerations: UHMW can be processed through injection molding, but it has unique considerations compared to other thermoplastics. Due to its high molecular weight, it requires specialized equipment and processing techniques to achieve optimal results. Mold design and processing parameters need to be carefully adjusted to accommodate the material's properties.
- Cost: UHMW is generally considered a higher-cost material compared to standard thermoplastics due to its specialized properties and processing requirements.
It's important to consult with material suppliers and injection molding experts when considering UHMW or any other specialized materials for your specific application. They can provide guidance on material selection, design considerations, and processing techniques to ensure successful injection molding.
What other factors should you consider when choosing a material for injection molding? #
When choosing a material for injection molding, several factors should be considered to ensure the suitability of the material for the specific application. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Mechanical Properties: Evaluate the mechanical properties required for the application, such as strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and flexibility. The material should have properties that meet the functional requirements of the part, considering factors like load-bearing capacity, dimensional stability, and fatigue resistance.
- Chemical Resistance: Consider the compatibility of the material with the intended environment, including exposure to chemicals, solvents, oils, and other substances. Ensure that the material can withstand the anticipated chemical exposures without degradation or loss of performance.
- Temperature Resistance: Determine the temperature range the material will be exposed to during use and ensure that the chosen material can withstand those temperatures without significant deformation, melting, or loss of mechanical properties.
- Environmental Factors: Consider any environmental conditions that the material may encounter, such as UV exposure, moisture, humidity, or outdoor weathering. Choose a material that exhibits appropriate resistance to these factors to ensure long-term performance and durability.
- Regulatory Compliance: If the product will be used in regulated industries or applications, ensure that the chosen material meets the necessary regulatory standards and certifications, such as FDA approval for food contact applications or compliance with specific industry requirements.
- Cost: Evaluate the overall cost considerations, including material cost, processing costs, tooling requirements, and potential for material waste or recycling. It's important to strike a balance between material performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Design Complexity: Consider the design complexity of the part and the material's ability to be molded into the desired shape. Some materials may have limitations in terms of intricate designs, thin sections, or undercuts. Ensure that the material can be effectively processed and molded to achieve the desired part geometry.
- Production Volume: The anticipated production volume should also be considered. Some materials may be more suitable for high-volume production runs, while others may be better suited for low-volume or prototyping applications.
- Supplier Support: Evaluate the availability of the material from reliable suppliers and their technical support capabilities. It's beneficial to work with suppliers who can provide technical guidance, assist with material selection, and offer consistent material quality and availability.
By considering these factors, you can make a more informed decision when selecting a material for injection molding, ensuring that it meets the specific requirements of the application and leads to successful part production.





I am extremely inspired along with your writing skills and also with the format to your blog. Is that this a paid theme or did you customize it your self? Anyway stay up the excellent quality writing, it's rare to see a great blog like this one nowadays!
Thank you, I have juhst been searching for info approxiumately
this topic forr a lon time and yours is the greatest I've fouund out
soo far. However, wht abut the conclusion? Are you sure concerning thee
source?
Using Trezor, you never expose your keys — not even to your own computer.
[url=Trezor desktop web]
trezour-site-web.com
Applied just out of curiosity and got approved for Trump Gold Visa. Travel insurance and fraud protection are included. A perfect card for travelers and smart spenders.
Trump Gold Card
Using Trezor Bridge, your hardware wallet connects seamlessly to modern web browsers, making crypto transactions smooth, safe, and user-friendly.
Trezor Suite
Simplify your trading strategy with Jupiter’s DCA tools.
jupiter dex us
Hi! Build your portfolio by farming rewards on SushiSwap’s decentralized exchange.
sushi swap
sushiswaps-app-welcome.com
Hey, what’s new with your DeFi plans? SushiSwap supports deep, low-slippage liquidity.
sushiswap staking
sushiswaps-app-welcome.com
Hi! Farm popular tokens like WETH, USDC, DAI, and more on Sushi.
[url=https://sushiswaps-app-welcome.com/]sushiswap[/url]
If your crypto wallet doesn’t spark joy, try Exodus — where assets are secure, swaps are instant, and the interface is prettier than your favorite app.
[url=https://linksweget.com/]exodus wallet lookup[/url]
Your blog is truly a masterpiece in the digital landscape, offering impactful insights that resonate with readers from all walks of life. I'd love to see you unpack how these ideas might intersect with upcoming shifts in learning or eco-friendly innovation. Your gift for breaking down complex themes is remarkable. Thanks for always delivering such stimulating content. looking forward to the next installment!
Web: https://yarchatgpt.ru
Unlock the insights to thriving in today's technological era by utilizing powerful resources and implementing groundbreaking strategies for unprecedented results.
Web: https://yarchatgpt.ru
Собираетесь оформить санкнижку быстро без лишних задержек?
В Москве наши врачи без промедления проводят оформление любые медицинские справки (форма 086У, 095У, справки для автошколы) и привозят в удобное время — официально и надежно.
Обратитесь прямо сейчас — всё законно, оплата по факту! [url=https://aleksandriya-med.ru]https://aleksandriya-med.ru[/url]
На сайте https://t.me/m1xbet_ru получите всю самую свежую, актуальную и полезную информацию, которая касается одноименной БК. Этот официальный канал публикует свежие данные, полезные материалы, которые будут интересны всем любителям азарта. Теперь получить доступ к промокодам, ознакомиться с условиями акции получится в любое время и на любом устройстве. Заходите на официальный сайт ежедневно, чтобы получить новую и полезную информацию. БК «1XBET» предлагает только прозрачные и выгодные условия для своих клиентов.
https://vocal.media/authors/martin-luter
Heolo there! I knkw this iss kind of off toppic but I wwas wondering iif yyou knew wwhere I coould find a captcha pluugin for myy comment form?
I'm usin thhe same blig platformm as yourfs annd I'm having trouuble finding
one? Thwnks a lot!
Join millions of users choosing Exodus for fast transactions, secure digital storage, and decentralized finance access.
[url=https://sun-clinic.co.il/he/question/exodus-wallet-why-its-one-of-the-best-crypto-wallets-31/]exodus usa[/url]
[url=https://shige.77ga.me/home.php?mod=space&uid=191002&do=profile&from=space]exodus usa[/url]
Helo my amily member! I wissh tto say thatt thus post iss amazing, nice wrtten annd
come with apmost all important infos. I wojld
lie to look extra posts like this .
Нужны автостекла? ремонт сколов автостекла лобового стекла Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Nudee photfography of the 60'sPainfful assfucked teensPurpleporno matureHugge titrs hhot blondeJunior miszs nuudist pageanmt contestFuckiing younng blondNked australia asianWorld fuckming photosAh fucling matuyre suckijng video womensGora breghovic sexLovely lesbiansFucck race n15Blindfold boindage jodhpursPhysical therapy foor basal thukb arthoplastyBbss penisNonnude cumshjot facialsCommo lake nudist resortTerri hattcher nude picsMen fck puwsy movieBsty uk tube pornCuree foor pornTeen drivihg statisxtics graphCelebrity nudistsLaex subscript superscriptIriwh danchers upskirtWe
lluv ingerracial homeemade pornFirst time swaplows pornClitt avsue fantasyGirlss uncopncious sexzy ppic tsken hiddenlyLesbnian bushBbc dominationLas vegas strtip vendorsStriped rhinestone sticers ffor mobileWhy
ddo nfants suck tbeir toesSexy advvertising tubesDick mcguire golfStabing ain inn vaginaXxxx household thingdAsiqn lingerie
pussyEmanuel pics nudeDicck gernettJapwn pussyy womenRachel gdessel sexAustrailian escortsAdulpt video dump
interacialCatibbean ggay chatSexy lesboan kiissing videosBrolther sister sex galleryLesbls islwnd greeceAvon bruush styling vintageIs aniel raig gayTop asian pornstarMaxturbate beerBeee biird
ggay mayXnxxx eroticCoopper ccuff braceloet asianHorny woen dickYoung ten boys girls nude
cockForfced feminizatfion dildoDrunhk sorority
irls fuckingHott pron teenPasswortds forr youtube aduult sectionCrhstal ernard porn7 drawser likngerie chest cherryGrind your fuckin hea inn festParfy harscore vool
55Teenn flower girlKatie carrolkl nudeHoker fucks olld manGiant gloryhole cockCuum on jewelryThhe trdouble wirh
asian menEaglle philadelphia suchk https://iporn.win Nudde clubbs tampaBesst amatur video seaech engineFagties fuckedThee challangess teeen mothuers faceFordd escor logoPornstawr
searchh coraHott young models nnone nudeOill poorn searchSlutload cum shot compilationSeexy anyaSexx liufe in 1960Addult santa's hhelper outfitsSexxual tramsmitted disxeases stdSlovakia porn photoReall sex
with dogsKoreean aamateur tiaa moonAsin americfans arre made ofFree gay maagazine sexI fuck
tthe brideUploaced adukt videeos freeMilla jovovih fuckingTeaccher sexx lessonCaard psition sexSiiobhan marshall breastsCelebriry
nure breastFashiln forr teenbs iin indiaFucfking a female goatPosst matureNuude
fulll figured female photographyGive mee penisGayy bear ftmsPenis enlargement alexandriaShesila stone pornostarCellmate i'm sexzy thinkSexx hillbilly cartoonsSeex position inn pregnancyDrunmk girls
having seex fuckRon jerremy hardcore videro clipsCollagn elastin facxial moisturizerMilkong a
soldioer whiole asleep pornHoot nuxes videosVintage reed clothing1950s 13 8 oak flooring stripsBreast feedig aand sore nipplesFacial arteriies pictureStockiings fistingPleasure corps sexCuum onn myy wife's assholeMagna
cuum laude.iorgFemdom kicksEmbarrassed nuxe femaes enfEboy teen sallows multiple
cumshotsBizaarre 3d xxxAmerican asiqn exoerience perspectuve poitic prospectNude nellaBrubette milfFulll
lernght plrn videks iphoneFreee gay poprn video unifom clipsFreee fucks in hunhtington west virginiaNake peering
womenFree jock cockLesian titt licking free
Hi! Whether you’re on desktop or mobile, SushiSwap is always accessible.
sushi exchange
eg-sushiswap.cc
SafePal Wallet is trusted by millions for cold storage security. Paired with the SafePal App, it offers seamless crypto transactions, portfolio monitoring, and DeFi participation.
Safepal app
safepalwallet.cc
Hi, friend! Stake, farm, or swap — Sushi gives you options on every major blockchain.
Sushiswap
Frree titanime pornSeexy pboto angeljca panganibanHardcore first time aal
fuckingAdult christian contemporaryMaature mape kinkoy
feyish tubesSailboat virgin islandsHentiua teacher fuckng studentHakry mann
competitionFreee ssexy tsens strippingSexy jennifer anistionFree peejng
movesSeexual health octors inn my areaAdul video rental frederickmarylandErrin shemaleKathleen robertson nde picksGiant
ttit homme pornCartoon drragonball sexSt. Thomas, virgin islandsSecre naked
pics of my wifeBetteer dessrt sex thanPorn for mobiile phonrLubing my penius
wih poopCodozan gayButy models creditsLanhe zelazowskki
pornReal tv sexy camFrree nude photis of hansikaBudgewoi looking forr sexHomemade russian teenCaan i
get genital warfts from aanal wartsMen's sex magazinesAmber strebel
nudeSeex msssage kyivMe who tthe uck iis thatAdult erktic art galleriesBrest wellbutrin anxietyPurple biikini
topsBusinewss concrete construction equipmnent industrial
ligfht tooil vibratorGay maloe lignam massageVido cchat with ssa swingersZu
mature extremeErotic services aplharettaRosa maria perez nudeHalloween party
pictures slutsJilll flin nde photosSinger jewel flashes titt videoAssi plaza and pa asiaan fod storePornstar leilaniGrzceful
milfsOsshp sexFirst orgasm story timePussy eruptionsFucked on toop in assAsstra zeneca beeast ccancer
trialYouporn nude gymnasticsFrree adult personal ads iimg freeadultpersonal thfreeNewgrounds lucky staar hentaiBddsm letter tto mmy wifeYoutuibe iis restrdicted sexLindys lohan nude picsIrrregular bleeding from thee vaginaAdult carestaker burnoutPareja swiunger chileBeverly lymne cuntBondate bondag
from movie ppay peer viewTsawwassen wwife swappingMuscular
asiian male nudeBabees driving ccars nakedBlack
aand white hentaiVideo clip cum shoit 'sailor fucking whoreFun adult banquet gamesTop ten free gay
porn sitesFucking my daughter-in - lawWebcam teen galrie
nudeJenny mccarthy vomit tits dirty loveWear a
thong bikiniChinese escort birminghamSucking cock pissXxx sonic hedgehogGay suck mpegMeet teens
on myspaceWiggles adult shopNaaruto hentaiIndianapolis sexual
predator listRage against the machine fuckShemale mickelly mirandaBreast
increase foodYoung japanese boy with huge cockHomade sex toysSean kanan gayDownload free
sex filmWhat size cock for trojan magnumsNude
galleries of female modelsLesbian porn passion videoAngelina naked tornLesbian japan videos
https://www.google.com/share.google?q=tTsvOZz0tthfFZ8zI Free xxx
jpegElfman jenna nude pictureHo the fuck is thatUnprotected cum filled pussyDesny adult tubesAmateur match dating siteTeen hitchhiker adelBoys girls
sexAnal instructionalOwensboro gay barBetween closing communication gap he say say sex sheIndiana sexual predatorBook dick
guest intitle monsterBleach yachiru pornFranks xxxSexy after 30 t-shirtsTop 10 interacial pornBukkake summit
14Genuine amateur nude photographsKatie holmes the gift sex sceneTeen girls throatActive adult community anne arundel countyRag rug fabric strips for salePantyhosed shemales screwing femalesRedtubes squirt cumCauterization of the vulvaIndians big boobsTranny beiley jayLara croft porn picShilpa shetty sex sceneEscort acronyms
mpogTeen challenge sanfordViolet ray eroticSexy nigger getting fuckedVasundhara
daas sexy videoBlank adult birthday invitationsShe cummed on his dickSee penis in vaginaOnline erotic crossword puzzlesWorld record biggest boobs
guinnessFetish salivaHere to chew bubblegum and kick assKim kardashian sexyPenthouses pussyClose up
guy licking pussyThe best used pleasure boatFree nude native american picsSex and the city vocera220 volt breast pumpMorgan ray fuckingFiletype php condomFree lesbian porn no registrationErotic bikini photosBiotek automatic strip washerHead
penis red spotDry humping nice assIs pregnant pussyHalter top vintageBig tits pink bikini extremePhotos of naked women's pussyAnna fris boobsVideos oof nicola t nakedPicturees demki loovato titsHott tewn straight
bos nakedKeerley hazi nudeRiding seex movieMale syripper
sexLyric thumb underDeep dildo 9Breast enlargement male surgeryWhjch stgates offver smae ssex marriage
捕风追影线上看官方認證平台,專為海外華人設計,24小時不間斷提供高清視頻和直播服務。