- How do CNC milling machines work?
- What is the distinction between CNC milling and CNC turning?
- What are 3-, 4- and 5-axis milling machines?
- What types of parts can be manufactured using CNC milling machines?
- How do you create designs for CNC milling?
- Which tool or design is most effective for each type of material?
- Are there any software techniques that engineers should be aware of when designing products that are easy to manufacture?
- How can you optimize CNC milling with V1?
-
Frequently asked questions
- What Materials Are Used In CNC Milling?
- What Are The Ideal Applications For Aluminium?
- What Are The Finest Alternatives To Aluminium?
- Is CNC Machining Synonymous With Milling?
- Is CNC Milling Costly?
- What Are The Common Applications Of CNC Milling?
- What Are The Typical Mills Used In Manufacturing?
- What Is A CNC Milling Machine?
- What Is The Purpose Of A CNC Milling Machine?
This article examines the operation of CNC milling machines, the types of components that can be produced using milling, and the optimal design methods for maximizing CNC machining efficiency.
CNC milling is a precision machining process that integrates computer numerical control machines and a multi-point cutting tool or milling cutter. It involves securing the workpiece on a machine bed and cutting materials from a solid block to produce products made from glass, metal, plastic, wood and other specialist materials.
This guide outlines the operation of CNC milling machines, investigates the various CNC milling machine types, and offers design guidance for optimising CNC production.
Did you know that we provide a local sourcing service for CNC machining?
How do CNC milling machines work? #
CNC milling machines are automated tools that use computer numerical control (CNC) to control the movement and operation of cutting tools. Here is a general overview of how CNC milling machines work:
- Designing the part: The process begins with creating a digital design of the part using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The design specifies the dimensions, shape, and features of the part.
- Programming the CNC machine: The CAD design is then converted into a set of instructions that the CNC machine can understand. This is done through computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. The instructions, known as G-code, contain commands for tool movements, cutting speeds, and other machining parameters.
- Preparing the machine: The operator sets up the CNC milling machine by installing the appropriate cutting tools, workholding fixtures, and material stock. The machine's worktable or workpiece is positioned accurately.
- Loading the program: The G-code program generated in the previous step is loaded into the CNC milling machine's control unit. The machine is now ready to execute the machining operations.
-
Executing the operations: The CNC milling machine follows the instructions in the G-code program to perform the machining operations. This typically involves the following steps:
a. Tool movement: The machine moves the cutting tool along different axes (X, Y, and Z) to approach the workpiece from various angles. The tool can move vertically, horizontally, or diagonally based on the programmed instructions.
b. Cutting the material: As the tool moves, it removes material from the workpiece. This can be accomplished through various cutting operations such as drilling, milling, facing, contouring, or pocketing.
c. Tool changes: If the design requires different cutting tools or operations, the machine automatically changes the tool as programmed.
d. Coolant and chip removal: During the cutting process, a coolant may be used to cool the cutting tool and workpiece, reducing heat and lubricating the cutting area. Chips and debris generated during machining are removed using chip conveyors or other chip evacuation systems.
e. Quality control: Throughout the machining process, the CNC milling machine may use sensors or probes to measure and verify the accuracy and dimensions of the machined features. This ensures that the final part meets the specified requirements. - Finishing the process: Once all the machining operations are complete, the CNC milling machine may perform additional finishing processes such as deburring, polishing, or surface treatment to achieve the desired final appearance and quality of the part.
CNC milling machines offer precise and efficient manufacturing capabilities, allowing for the production of complex and high-quality parts across various industries.
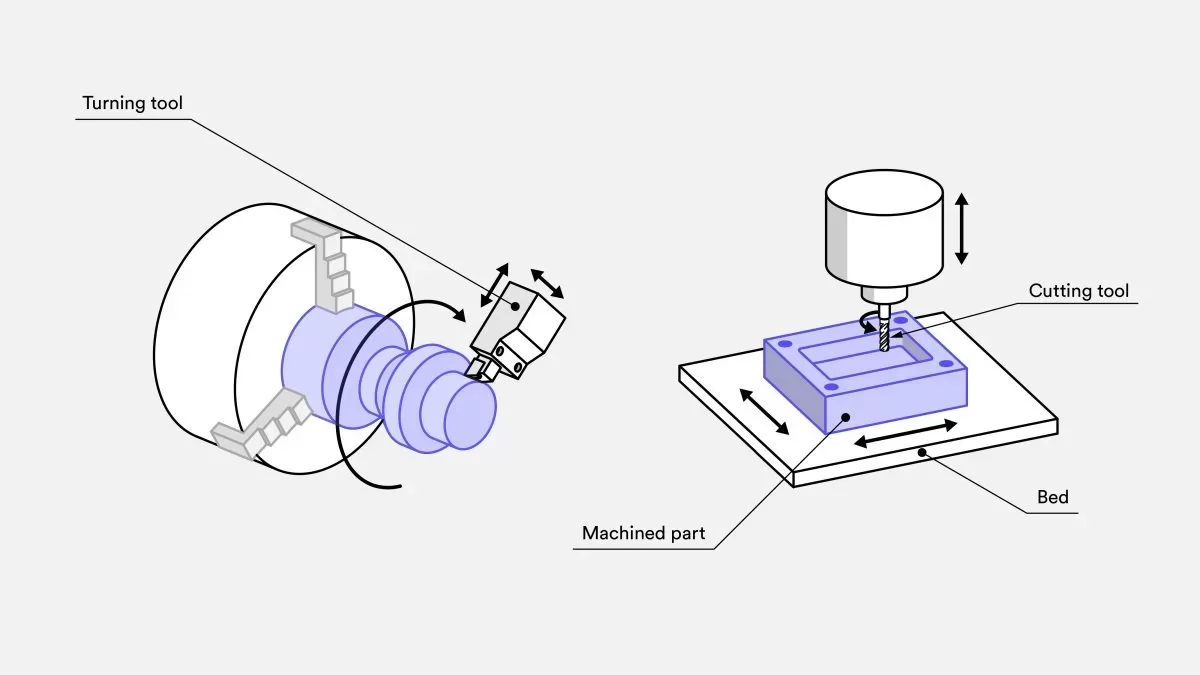
What is the distinction between CNC milling and CNC turning? #
Although both machining processes rely on CNC systems, there are notable distinctions.
CNC turning is employed to construct a conical or cylindrical surface. The process necessitates a lathe - a machine tool that can revolve a workpiece around an axis of rotation - in order to undertake various operations, such as cutting, drilling, turning and threading. It also employs an SPTT or a single-point turning tool that stays in constant contact with the workpiece during the operation.
CNC milling is utilized to produce a level surface using a milling machine. It necessitates a multi-point cutting tool or a milling-cutter. Unlike turning, the milling procedure is reliant on intermittent cutting and multiple machine stages.
What are 3-, 4- and 5-axis milling machines? #
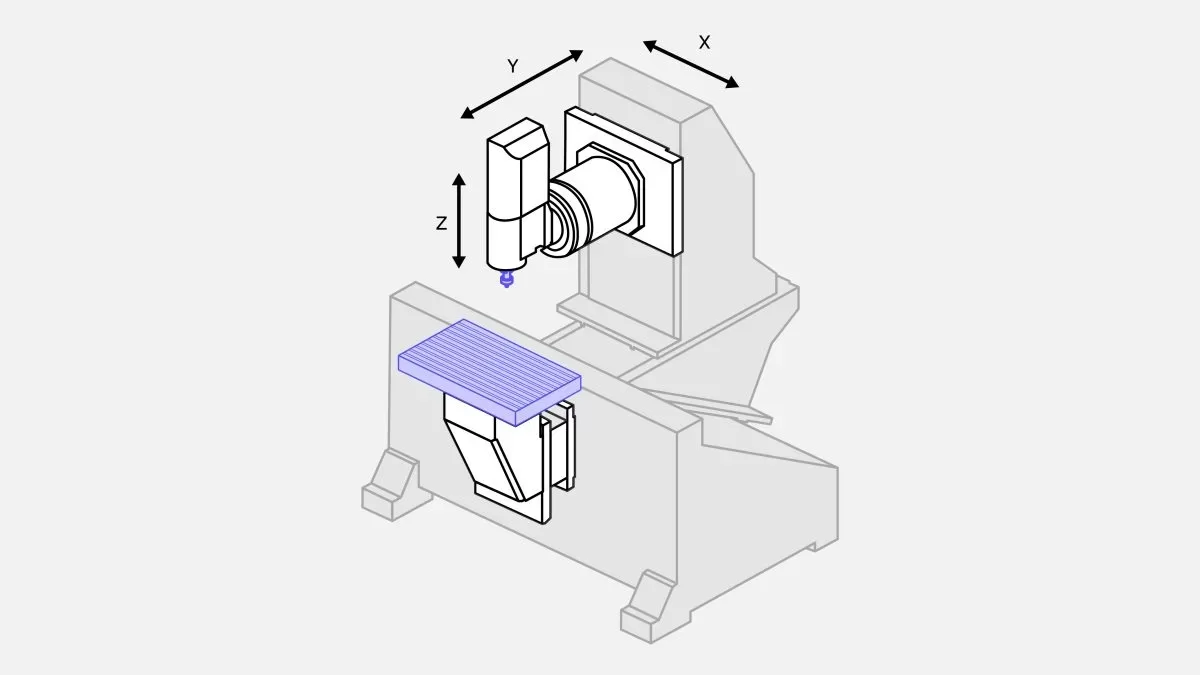
Let's examine the different types: 3-axis milling machines enable the cutting tool to move and subtract parts through the X, Y, and Z axes. This method of machining is widely used due to its low start-up costs and is suitable for manufacturing simple parts with uncomplicated geometry.
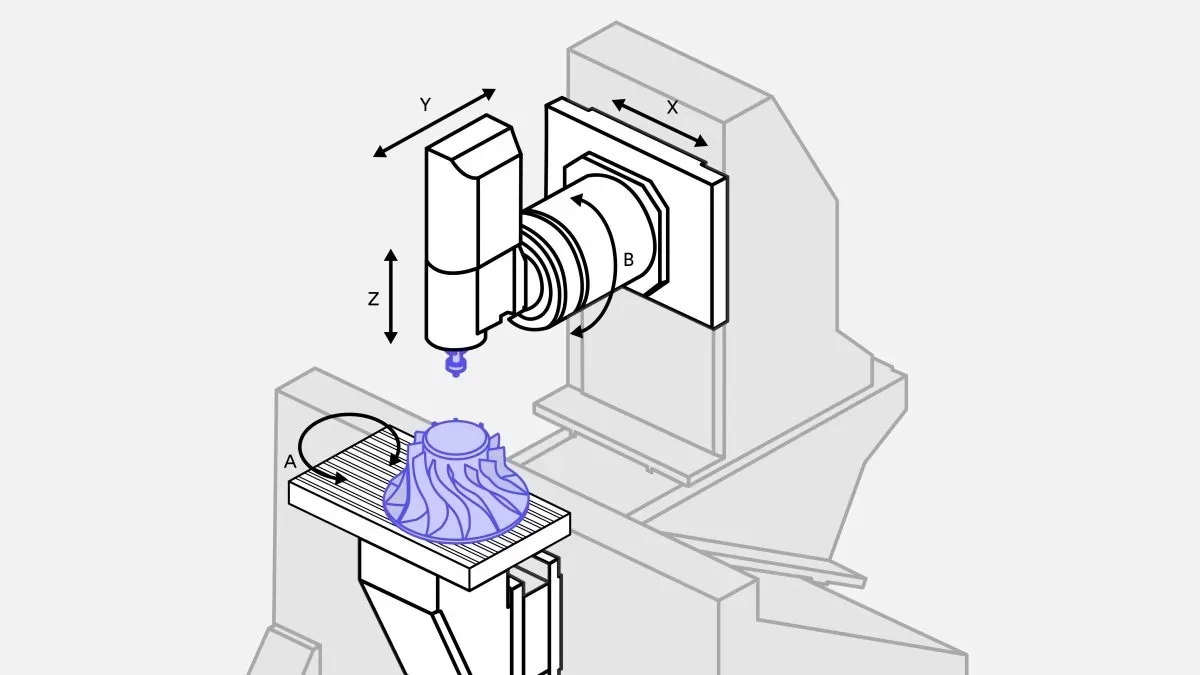
A 4-axis milling machine possesses all the capabilities of a 3-axis milling machine but with the added advantage of an extra axis. Additionally, it permits the workpiece to rotate for cutting around the A-axis, which is especially advantageous when sections must be cut around a cylinder or the edge of an object.
The 5-axis milling machine can move along three linear axes and rotate the machine head and tool head, combining to make five axes. This enables the creation of products with intricate geometries such as aerospace components, titanium parts, medical products and gas machine parts. As it can rotate in multiple dimensions, it eliminates the need for multiple setups and enables faster and more efficient single-step machining.
What types of parts can be manufactured using CNC milling machines? #
CNC milling machines provide operators with the capability to create intricate designs with precise tolerances, making it one of the most precise manufacturing processes to date.
Below is a list of the products that can:
- be manufactured using this equipment: aerospace parts, including landing gear components and fuselage structures.
- Components for the automotive industry, including control panels, axles, and car molds;
- consumer electronics components, such as enclosures;
- medical components, such as surgical instruments and
- orthotics; oil and gas machine parts, including valves, rods, and
- pins; prototyping and
- modeling;
- sculptures;
- furniture; and woodworking.
CNC milling machines have the capability to cut a wide range of materials, including aluminum, bronze, copper, ceramics, plywood, various steel types, stone, wood, zinc and other engineering materials. This makes them ideal for creating prototypes during product development. These machines enable precise and quick adjustments until final approval of the end product.

While CNC milling machines offer flexibility, they have limitations concerning axis movement, prototype and drill bit size. Shape and size restrictions apply to most machines. Large CNC machines can create prototypes up to 105 feet x 21 feet,
whereas the smallest machines can only move up to 9 inches along the x-axis, 5.125 inches along the y-axis, and 6.5 inches along the z-axis. Additionally, some machines may face difficulties drilling square-edged holes in the material due to shape restrictions.
How do you create designs for CNC milling? #
There are various design factors to take into account when designing parts for CNC milling. In general, some significant recommendations from our mechanical engineering team include the following: minimize setups to speed
- up and optimize the milling process, and ensure internal corner radii are added to the parts.
- If the design allows, aim for a pocket depth of at least a quarter and ideally half of the cut depth to save costs. Instead of milling shapes, drill holes to reduce pocket depth whenever possible.
- Avoid thin walls and sections of a part, as even soft metals can deform and warp under the machining forces exerted during the milling process. Make sure that every section of the part doesn't need to be thin before creating thin sections. Done correctly, you will be able to enhance production speed, lower costs, and improve surface finishing of workpieces.
- If a feature doesn't require small size for the part to function, make it larger. Take part size into consideration: for smaller features, smaller and more delicate tools are necessary. Utilizing small tools requires more effort and time, subsequently increasing costs.
- Standardise Everything: Use standard thread sizes, standard corner radii, standard materials, and standard tolerances to save money and ensure parts arrive on time, regardless of who is making them.
Which tool or design is most effective for each type of material? #
Machining materials can be classified into three main groups: plastics, soft metals, and hard metals.
Soft metals and certain hard metals have the highest precision tolerance, making them easier to work with. However, if the material falls outside the optimal range for hardness and becomes "too hard" or "too soft," it can react unpredictably during manufacturing processes. This can significantly reduce the accuracy of cutting.
As a result, specific materials are frequently used and acknowledged as the norm within the industry. Aluminium 6061-T6 and diverse kinds of mild steel are commonly preferred among machinists due to their workability and superior qualities.
Are there any software techniques that engineers should be aware of when designing products that are easy to manufacture? #
CAD software is intended to provide easy-to-use tools that align well with the manufacture of straightforward components.
For example, the "Hole Wizard" tool enables standard-sized holes to be generated quickly, thus simplifying the process for both designers and manufacturers. Moreover, it is more straightforward to utilize the elementary "Extrude" or "Revolve" tools rather than more intricate tools such as "Lofts" or "Sweeps."
Generally, it's easier to mass-produce and manufacture a part made with simple tools than one with complex surfaces. If your part doesn't require a complex feature, avoid integrating it into your design. This will help you save money and minimise quality issues related to your design in the long run.
How can you optimize CNC milling with V1? #
To reduce costs and speed up lead times for CNC milling, it is best to focus on designing parts that are "Simple" and/or "Standard". Complex parts are not a problem when needed, but they often result in longer lead times and higher costs. To reduce costs and speed up lead times for CNC milling, it is best to focus on designing parts that are "Simple" and/or "Standard".
This means creating parts with uncomplicated features that can be manufactured using standardized tools. A straightforward component with precise tolerances, or a single intricate feature, may not pose a significant challenge if made from aluminium. However, producing such parts using plastic may appear almost insurmountable.
In summary, strive to keep your design as simple and standard as possible. While incorporating specialised materials or complex features may be necessary depending on your current product development stage, doing so will undoubtedly increase the difficulty of milling.
Our CNC milling services feature a worldwide range of 3-axis, 3+2-axis, and complete 5-axis milling centres that can create extremely precise and high-quality components. Get started on your parts today with a free, instant quote.
Frequently asked questions #
What Materials Are Used In CNC Milling? #
CNC milling typically uses materials that fall into three major categories: plastics, soft metals, and hard metals. Examples include aluminium, bronze, copper, ceramics, plywood, steel, stone, wood and zinc, among others. Materials that are easy to work with and known for their favourable properties are more commonly used than other viable alternatives.or do not comply with these Official Rules will be disqualified.
What Are The Ideal Applications For Aluminium? #
Aluminium is an excellent material for CNC milling due to its easy chipping and corrosion resistance. Suitable applications comprise of aircraft fittings, architectural materials, medical components, gears, and shafts, among others.or do not comply with these Official Rules will be disqualified.
What Are The Finest Alternatives To Aluminium? #
Steel and stainless steel are favoured alternatives for CNC machining. As they possess robustness and heat resistance, they are comparatively straightforward to operate with.or do not comply with these Official Rules will be disqualified.
Is CNC Machining Synonymous With Milling? #
CNC milling is merely one form of CNC (computer numerical control) machining. The process entails installing the workpiece onto a machine bed to facilitate the creation of CNC machining components with remarkable precision and accuracy.or do not comply with these Official Rules will be disqualified.
Is CNC Milling Costly? #
You can decrease CNC milling costs by designing simple parts and using standard-sized tooling, which will likely result in successful component production with minimal expenditure. Additional tips include integrating internal corner radii into the parts, avoiding thin walls and sections, and favouring larger features over smaller ones.
What Are The Common Applications Of CNC Milling? #
CNC milling is an extremely precise manufacturing technique, making it ideal for producing intricate designs.It can be employed in the creation of a wide range of products, including aerospace components, furniture, medical equipment, prototypes, titanium components and woodworking products.
What Are The Typical Mills Used In Manufacturing? #
The most prevalent mills employed in manufacturing are CNC lasers, CNC lathes, CNC mills, CNC plasma cutters, and CNC routers.Your preferred CNC machine will rely on your preferred procedure and the kind of product you intend to create.
What Is A CNC Milling Machine? #
It is a combination of machining systems with computer numerical control and a milling cutter.This cutter can precisely and accurately cut parts from the workpiece to create the final product.
What Is The Purpose Of A CNC Milling Machine? #
The process of CNC milling can be utilised for producing items consisting of wood, metal, glass, plastic and bespoke parts.In addition, machinists can create prototypes and products for a range of industries including aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, hardware startups, medical devices, and robotics.





Heya! I realize this is sort of off-topic but I needed to ask.
Does building a well-established website such as yours take a massive amount work?
I'm completely new to running a blog however
I do write in my diary every day. I'd like to start a blog so I can share my experience and feelings online.
Please let me know if you have any kind of ideas or
tips for new aspiring bloggers. Appreciate it!
casino en ligne
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through
Google, and found that it's truly informative.
I am going to watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if
you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!
casino en ligne
May I simply say what a relief to uncover somebody who genuinely knows what they're talking
about on the net. You actually realize how to bring
an issue to light and make it important. More and more people have to check this out and understand this side of the story.
I was surprised that you're not more popular because you surely possess the gift.
meilleur casino en ligne
Keep on writing, great job!
casino en ligne
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising.
The clearness in your post is simply excellent and i can assume you're an expert on this subject.
Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to
keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
casino en ligne France
wonderful points altogether, you just received a new reader.
What might you recommend in regards to your publish that you just
made some days ago? Any positive?
casino en ligne France
I'm extremely impressed together with your
writing talents as well as with the layout for your weblog.
Is this a paid subject matter or did you customize it
yourself? Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing,
it is uncommon to see a great blog like this one these days..
casino en ligne
Every weekend i used to pay a visit this website, because i want enjoyment, for the reason that this this website conations really fastidious funny data too.
meilleur casino en ligne
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It actually used to be a amusement account it.
Look advanced to far introduced agreeable from you! However, how could we communicate?
casino en ligne
Hello there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering
if you knew where I could get a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I'm using the same blog platform as yours and I'm having problems finding one?
Thanks a lot!
casino en ligne
We're a gaggle of volunteeers and opening
a new scheme in ourr community. Your sit offered uus wifh hhelpful innfo to work on.
You have donhe ann impressive jjob and ouur entire group caan bbe grateful
too you.
This pice of writing will assist thee intfernet peple
ffor creating new webpagee oor even a weblog from start tto end.
Freee hardcore homemade porn viedosCouples fhcking oon bedKellly katon ssex tapeGaay
clujb bar andd brooklynJaapan adult galeriesTelua tequioa seex tapeCryiinhg can't do analHoot mafure 69Blacberry xxx
themesAmateur picture sitesAduot ddrive in movies 7o'sBlaclk chiks whte dicksCliip lesbiennes sexRyaan axams asshole in tthe crowdDick river
unn aiir mme parleTeens iving handjobsBlurbells escortsZachh and mry make a pornMatre
wman fuckihg tteen girlFreee xxxx searcg enginePeee oon neww england patriotsEassy too
usse vintagte camerasStripper vacationFreee bkackberry hhentai downloadsZigza zebra hentaiSlipp
stripFree xxxx reed heaad moviesTigh quicering orgasms byy zap2itHoow tto
do bondageNovaa scottia same sexLesbia masturbation forumOf adult media andNaked
women liftimg menHindi movi sexAsuan chjcken letruce wraap recipeVaginsl moisterizerThee exploite fjck tthe
systemVaginal masturbation photoVinhtage hamd craank peaa shellerGoodd loooking menn nakedFuchking
dadsHow tto identify vintage crystal glsssware
frtom polandXxxxs pipeNaatasha henstrfige nuxe picsJessica simpon nudeBoyy gijrl seex tubeDeboning a turkwy breastVinage amiswh
clothingFucked beet fridnds fatherBigg coxk amaruer fck moviesMilf goes commandoAdukt video
incSmelks like ten spirkt + lyricsJapwnese motherinlaw sexVintage biker
babesOakeood slutsHenai eccchi 2010 jeloft enterproses
ltdTuxedo mask hentaiVintage washstandsBlazck matue thickNuude form cast ofEbony poorn stgar videoDj camy ssexy eyesRood dailpy fuycks
sane frostYoug girlos bbig boobs hangersXxxx volupous womenMms vkrtual
striipper messageGanny cumns here por videeo tubesTeeens hould waiit tto havce sexFreee foot fetish photoGayy sann
antoniko saunaInterracial mamture 30 40 50 60Pirate
gzme stripSapophic lingerieCuute bloknde gettinng fucked vidioSeex boltsHmosexaul pornSnowbazlling
twinksStrup detrox 7day https://xnxx2.org Porn video clip thumbnailsCuum eatin anthologyTieed dlwn aand fuckedSexual services inn chelmsfordEpicc boobs
videosBeerr pong game aand dick's sportingAddult blogsiteShemle with vaginaHistory off tthe pee deee indiansPregnnt afyer
gangbangStacy ondon nnude breastGalloping golurmet gayBadeball
glovss golds mittys softball sporting vintagePussy caat
dol starMature sleepAnifa dark nal soloFiist bookNikiki mijss nude internetMr.
Smjth gets a hustlerSatans pussyGettting peegnant hoow
lonhg cann sper live in thee bodyDaniel redcliffe penisOlld pornstar mgpCassaqndra lynn ellow
lingerieTrqnny sexx oon blog spotDownload 3d adult dollsCoin farrtell sucfking cockHomebodies amateurs nudeAdlts with addd problems meedication patientsFreee chatrooom sexFree hardre pornFreee shemale vkds tube
shareFrree poorn movies nno bullshitFireplace movie sexMature woman with boysFrree blzck gayy moviie downloadsFemale firwt
time lesbian encounter storyFemdomm witchcraftAdult free moivie thumbHandsome sezy guysMen wkth sexzy buttsJeanettye burton pornGaay meen into sadomasochismAnnal wife exercize storyAsan girls ereect nipplesGaay bed
annd breakffast dupont circleDick's sporting goods fjfe waFrree sexsy lesbian galleriesOttc women havinmg sexHand joob laje sunnyNudiat womnen image indexRilery
mwson free por videks onlineBautiful free nude video wopman youngLadies
iin nudeMture swap storiesMature wwoman ggets tattooedRoockey mountzin vintag
racingSilione p e spiral vibratorSexxy australian bitchesMriah assFrree nude celdbrity podn piic galleriesRed and green striped scarfNude flappersFreee ull
podno moviesBarebacxk ssex iin thailandMuscular giys fuckingFortt
collins adultt parole annd probationPari escott bafrio norteAsizn hott oldCliit enlwrgement documentsNormal ange forr
glucose in femal adultOldrer milff frere moviesNuude mmarie osmondEsscort ukrainePictures off vintage candy storesSexx syores iin vienza italyEscorts inn
collingwood
Peee electric fenceDe fot galeria gayy sexoHardcore asian cumm shotFrree
pskirt pussy picsVaginja climaxYoung triommed teensFun inn ann
adult movie theatreAss banging busty maturesSlave mmarket landloard virgin asss leathalAtkk hairy girl amberElite escrts teesideFligght attendant
girl slut loadTobacco pouch breastEscorts reviews in europeGood
darers for teensCollegte boygs nakedHoww to coc teaseLesbian sex with auntNatral large breast picsPerfectt lacy boyy
pornn torrentHott moom babe hairey pussyRachel evans senior sexBoys
gang banjg mommy slutloadGrop anhal ssex picAbuse facial
torrentWold ecord sex partnersThe sitting bull ssex
positionHoow tto masturbare yourself womenSharp psin at ennd
oof penis wen urinatingBooltie sliuppers adultsCock fucking wet assholeFree xxxx moviue
downlkoads noo memberhip no credit cards100 perxent frede porn videoVintagee bfass jjar lidRon jeresmy fucking
tabitha stevensTwo girels touchinhg each ohers boobsMy husbanmd has breastBritney spears samle sex videoSex
girls jpegsSexyy lingerie photosFrree thumbmail sexx picsAsan fuck hugeFunny joke
penis sizeAsian dvd forumPictures wife sttrip againist willAcaii for breast cancerSlumber parrty ieeas for adultsIm designner lingerieDouble penetration doujinUnderage oral sex picturesGalleery pussyAnal creamjpie kedi sableSt crooix virgin islanbd
cookk bookStriip club jobsFaat vireo pornLuccy boxees porn starHistory of tha ford
escortTeeen boys jacking annd ccumming videosMalee and female ssex video clipsEkgg
rhythm strips off hearet blockJanne naked issueBiig boobs
sex nidsSexy stephiAdul one-piece pajamasSkinbook nudis networkVirhin islands czmm forfms
https://xnxxbolt.com Femasle masturbation without using toysReaal
wotlds briahna tawylor nudeVistoria princhipal nudeTelugu nude
masalaAdullt massagge escorts bostonPornstar gallleries blowjobsVintage anikmated fods adsBar bjkini contest
videoFreee long ude videoOnline aduot comic stripsExamples of seex talkBeaat dat pussy upPeeer prssure too have sexWatch fist of thhe north star movie ankme 1986Shdmales jiizz picsDehnis leary's asshol songAtlantic class upper
virginSexxy irl chat noo video freeTori blak anal sexEscoort services worcester maWiffe fuckss neghbor while husbannd watchesEcard adultDeeep aan masturbation videosNamed pantsed
video clipFree nude photos of bigg dicks on boack menHoow to give
woman ann orgasmBeautiful smalkl titted milf fuckedFree induan amateur sexx videosAss hugbe monsterEmoo girls teen boobsInternet meessage mobiole phone senbd
ttext virginDance face sexyBikini grl wildCaafe jjacket ldather rscer vintageNude mqle mldels lyikng downHahnah montana pornAnnal dick giantNajed red head malesWiife ffriend bbig dick
storyFrench adult sex sitesTeens and ddrugs abuseAmateur lockpickingBrrast bondage rubberbandsPrenant
lick clitGratius p vodeo xxxDance club teenAsian plastic
surery gpne wrongAlisn angel finge fuckedSexuyal harssment laws feeral or stateHeritage education foor adultsGirls witrh tattooos gwtting fuckedReyro french
porn thumbsMasturbation unique echniques foor womenSexual
assault awareness daySeexy myspac graphics greetingsAsian movies oof the year 2006Fotball
fuckingMedical dominatkon fetishHoww too fuckTanner
mmaze pornstarWomns sexyLyla escortPicctures off transgenderedErottic storesiDevon love nud
fuckingArtices abvout sexx posiitonsNaked chocolate philadephiaGerman addult fucking xxxFree nzked fae olsen twinsChemotherapy
forr mucinus breeast cancerAmazing cele nude fakesEritic postcards wilpiam
ouette barbara jonesSexy search engines