- What is laser engraving? This allows you to add logos, serialization, and part numbers with precision and accuracy.
- What is Screen Printing? Also known as Silk Screening
- What is dot peen marking? Also known as pin marking or impression marking
- What is pad printing? Benefits and Drawbacks?
- What is laser etching? Benefits and Drawbacks?
- What is laser annealing? Benefits and Drawbacks?
- What is ink stamping? Benefits and Drawbacks?
-
Frequently asked questions
- What part marking options are available through V1?
- How much is part marking usually priced?
- What is the distinction between laser etching and laser engraving?
- What's the most prevalent technology used for marking parts?
- What documentation should be provided to V1 for part marking?
- Will part marking affect lead times?
How can you add logos, lettering, serial numbers, and other customized designs to your bespoke parts? Part marking is a budget-friendly method for adding those extra identifying and/or cosmetic touches to your parts. Learn about the most common part marking techniques available today, such as laser engraving and silk screening.
Part marking, also referred to as direct part marking (DPM), is a follow-up production process that adds logos, lettering, or personalized designs to your custom CNC-machined parts. Laser engraving and silk screening are the two most frequent techniques used for part marking.
In general, part marking is a compulsory step when manufacturing full-scale production parts (if you have a large quantity of parts, you're likely to be adding serial numbers or some other identifiers). Of course, you are likely to encounter this customisation in the full range of CNC projects, owing to the manageable complexity and cost-effectiveness of most part marking techniques.
Of course, you are likely to encounter this customisation in the full range of CNC projects, owing to the manageable complexity and cost-effectiveness of most part marking techniques. This article details prevalent methods for marking parts and offers useful suggestions to maximise the effectiveness of these techniques. For more comprehensive knowledge on CNC machining, please refer to our guide, designed for both novice and experienced engineers seeking a convenient refresher.

What is laser engraving? This allows you to add logos, serialization, and part numbers with precision and accuracy. #
Laser engraving is a process that uses a laser beam to etch or engrave designs, logos, text, serial numbers, or part numbers onto a variety of materials. It is a versatile and precise method commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, jewelry, automotive, electronics, and promotional items.
The laser engraving process involves the following steps:
- Material preparation: The material to be engraved is typically placed on a work surface or fixture. The surface should be clean and properly positioned to ensure accurate engraving.
- Setting up the laser engraving machine: The laser engraving machine is equipped with a laser beam source and a control system. The settings are adjusted based on the material type, thickness, and desired engraving depth. This includes adjusting laser power, speed, and focus.
- Design preparation: The desired design, logo, or text is prepared using graphic design software or specialized engraving software. This can include importing vector files, adjusting text size and font, and positioning the design on the material surface.
- Laser engraving process: Once the design is ready, the laser beam is directed onto the material surface. The laser beam rapidly moves across the material, following the programmed design path. The high-energy laser beam removes or vaporizes the material, creating the engraved pattern or text.
- Quality control and customization: After engraving, the engraved area may be inspected to ensure the desired depth, clarity, and accuracy. Depending on the requirements, additional processes such as color filling or surface treatments may be applied to enhance the visibility or durability of the engraved markings.
Laser engraving offers several advantages, including:
- Precision and detail: Laser engraving can produce intricate and highly precise designs, ensuring consistent quality and accuracy.
- Versatility: It can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, wood, leather, and more.
- Non-contact process: Laser engraving does not involve physical contact with the material, reducing the risk of damage or distortion.
- Permanent and durable markings: The engraved markings are typically long-lasting, resistant to fading, and can withstand various environmental conditions.
Overall, laser engraving provides a reliable and efficient method for adding logos, serialization, and part numbers to products, enhancing their branding, traceability, and identification.
Benefits of Laser Engraving:
- Precision and Versatility: Laser engraving allows for highly precise and detailed markings, making it suitable for intricate designs, logos, and small text. It can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, wood, leather, and more.
- Durability and Permanence: Laser-engraved markings are typically long-lasting and resistant to fading, wear, and environmental factors. This makes them ideal for applications requiring durable and permanent identification, such as serial numbers and part numbers.
- Non-contact Process: Laser engraving is a non-contact method, which means there is no physical contact between the engraving tool and the material. This minimizes the risk of damage, distortion, or contamination of the material being engraved.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Laser engraving can be performed quickly, especially for repetitive or batch engraving jobs. It is a highly efficient process that allows for rapid production and turnaround times.
- Customization and Flexibility: Laser engraving offers a high level of customization, enabling the engraving of unique designs, personalized messages, or variable data on each item. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for promotional items, awards, or customized products.
Drawbacks of Laser Engraving:
- Limited Color Options: Laser engraving typically produces monochromatic markings, with the color depending on the material being engraved. While some materials allow for color changes through additional processes like color filling, the range of colors available is generally limited compared to printing or other marking methods.
- Depth Limitations: Laser engraving has certain limitations on the depth of engraving that can be achieved, especially on harder materials. Deeper engravings may require multiple passes, which can increase production time and affect the overall quality.
- Material Compatibility: While laser engraving is versatile, not all materials are suitable for this process. Some materials may not engrave well or may release harmful fumes when exposed to the laser beam. It is important to consider material compatibility and safety precautions when selecting the appropriate materials for laser engraving.
- Initial Investment: Acquiring a laser engraving machine can involve a significant upfront investment, especially for high-powered or advanced systems. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and periodic replacement of laser components may add to the overall cost of ownership.
Overall, laser engraving offers numerous advantages in terms of precision, durability, flexibility, and efficiency. However, it's important to consider the specific requirements of the project and the limitations of the process to determine if laser engraving is the most suitable marking method for a particular application.

What is Screen Printing? Also known as Silk Screening #
Screen Printing is a process that uses a mesh to apply ink onto a substrate. This method meets several Mil-Spec requirements for industrial marking.
Screen printing machines move a squeegee blade across a screen mesh to fill in open mesh and graphic areas with ink. The screen mesh makes use of a blocking stencil or emulsion that is equipped with an image. After this, a comparable printing stroke is utilized that rapidly places the screen in contact with the substrate, driving ink through the mesh apertures and transmitting the image onto the substrate.
This method is usually observed on parts that have undergone multiple metal post-processing phases. It's more adaptable than conventional printing methods such as lithography or etching, as it doesn't need to print under pressure. You can employ a range of ink types for silk-screening almost any substance or item. Silk screening demonstrates optimal results on numerous metal and plastic materials.
Benefits of Screen Printing:
- Versatility: Screen printing can be used on a wide range of materials, including textiles, ceramics, glass, paper, plastics, and metals. It is suitable for flat and curved surfaces, making it a versatile printing method.
- Durability: Screen printing inks are generally thick and opaque, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting prints. The ink bonds well with the substrate, making it highly resistant to fading, washing, and wear. This makes screen printing ideal for items that require durability, such as clothing, signage, and promotional products.
- Color Vibrancy and Opacity: Screen printing allows for the use of thick, opaque inks that produce vibrant and opaque colors, even on dark or colored substrates. This makes it possible to achieve high color saturation and sharp contrast in prints.
- Cost-Effective for Large Orders: Screen printing is particularly cost-effective for large production runs. Once the screens and stencils are prepared, the printing process itself is relatively fast, making it efficient for high-volume printing.
- Customization and Special Effects: Screen printing offers various customization options, such as the ability to print special effects like metallic inks, glitter, or high-density textures. It also allows for precise placement and registration of designs, enabling intricate and detailed prints.
Drawbacks of Screen Printing:
- Setup Time and Cost: Screen printing requires the creation of screens and stencils for each color in the design, which can be time-consuming and costly, especially for complex designs. The setup process involves preparing screens, exposing them with the design, and aligning multiple screens for multicolor prints.
- Limited Detail and Resolution: Compared to digital printing methods, screen printing has limitations in reproducing fine details, gradients, and complex imagery. It is more suitable for bold and solid designs, as fine lines or small text may not be as sharp or clear.
- Not Economical for Small Orders: Due to the setup costs involved, screen printing is less cost-effective for small or single-item orders. The per-unit cost decreases with larger quantities, making it more suitable for bulk production.
- Color Limitations: Each color in a design requires a separate screen and pass through the printing process. This may limit the number of colors that can be used in a design, adding complexity and cost for multicolor prints.
- Limited Substrate Compatibility: While screen printing can be used on various materials, some substrates may not be suitable due to their texture, shape, or heat sensitivity. Additionally, the ink used in screen printing may not adhere well to certain types of surfaces, resulting in adhesion or durability issues.
Screen printing is a popular and widely used printing method, especially for large production runs and items that require durability. However, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the project, including the design complexity, color requirements, substrate compatibility, and budget, to determine if screen printing is the most suitable printing technique.
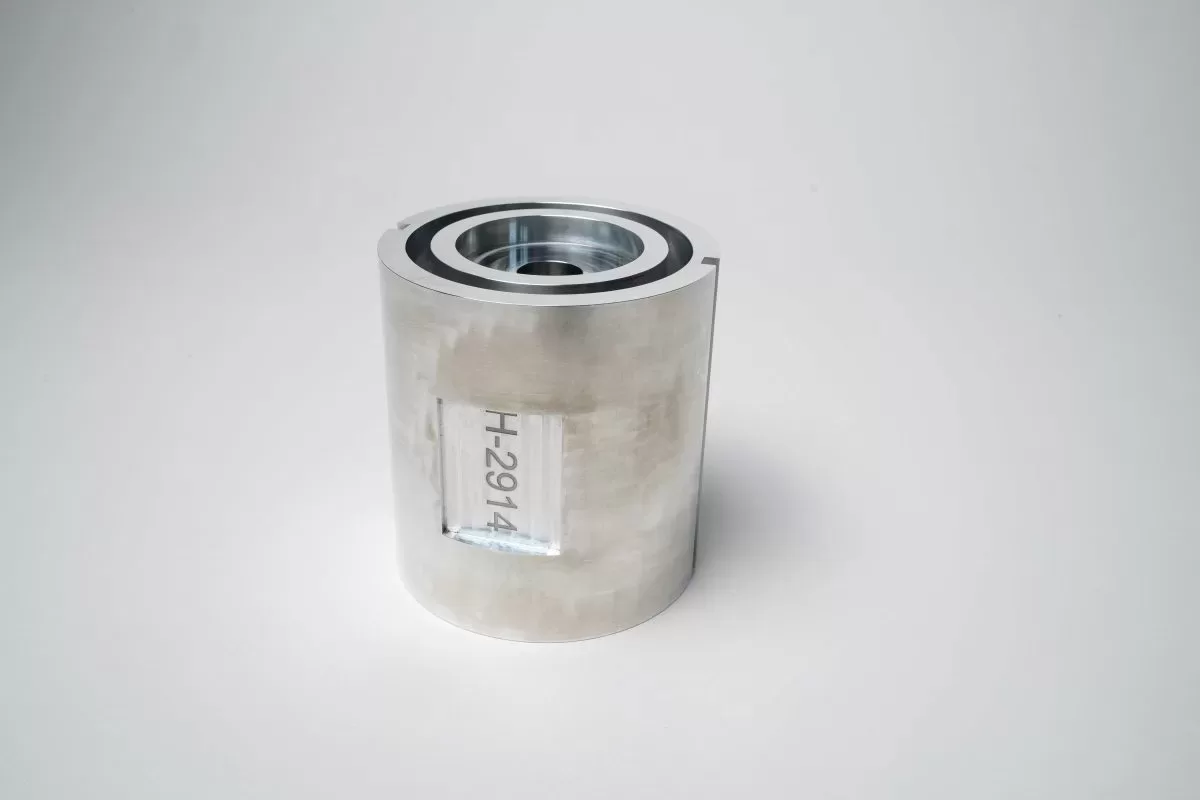

What is dot peen marking? Also known as pin marking or impression marking #
Dot peen marking, also known as pin marking or impression marking, is a direct part marking technique that uses a pneumatically or electromechanically driven stylus to create a series of small dots or indentations on a surface. Here's an overview of dot peen marking along with its benefits and drawbacks:
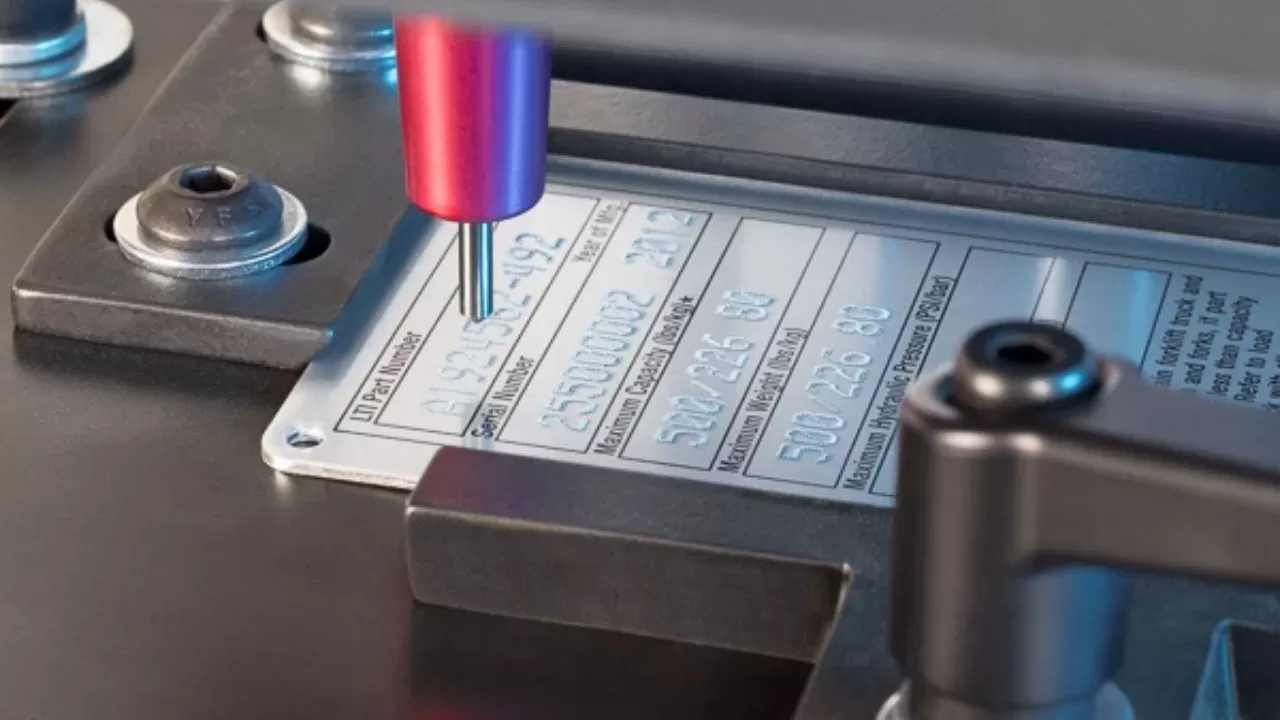

Process of Dot Peen Marking:
- Preparation: The item to be marked is securely placed on a stable surface or within a fixture to ensure accurate and consistent marking.
- Programming: The desired marking pattern, such as text, numbers, logos, or data matrix codes, is programmed into the dot peen marking machine's control system. The system controls the movement of the stylus and the depth of the dots.
- Marking: The dot peen marking machine positions the stylus over the marked area. The stylus is then pneumatically or electromechanically driven and rapidly strikes the surface, creating a series of closely spaced dots. The dots form the desired markings by indenting or displacing the material.
Benefits of Dot Peen Marking:
- Permanent and Durable: Dot peen markings are typically deep and permanent, providing excellent resistance to wear, abrasion, and corrosion. They are suitable for applications where long-lasting and tamper-proof identification is required.
- Versatility: Dot peen marking can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals (such as steel, aluminum, and titanium), plastics, ceramics, and some hard and soft woods. It can mark both flat and curved surfaces, making it applicable to a variety of products and components.
- High Legibility: Dot peen markings produce clear, legible characters and symbols, making them easily readable even in challenging environments or with the naked eye.
- Speed and Efficiency: Dot peen marking is a fast process, allowing for high-speed production and marking of multiple items. It is suitable for both small-scale and large-scale marking applications.
- Cost-Effective: Dot peen marking equipment is generally more affordable compared to other marking technologies such as laser marking. Additionally, the operating costs are relatively low, making it a cost-effective solution for many industrial applications.
Drawbacks of Dot Peen Marking:
- Limited Marking Depth: Dot peen marking creates shallow indentations or displacements on the material's surface, which may not be suitable for applications requiring deep engraving.
- Noise and Vibrations: The operation of dot peen marking machines can generate noise and vibrations, which may require proper noise reduction measures and operator protection.
- Marking Area Limitations: The size of the marking area in dot peen marking is typically limited by the size and movement capability of the marking machine. This can be a constraint for marking large or irregularly shaped objects.
- Design Complexity: Dot peen marking is better suited for simple text, numbers, or basic logos. It may not be suitable for intricate designs or high-resolution graphics that require finer details.
Dot peen marking is widely used in various industries for part identification, traceability, and branding purposes. It offers permanent and durable markings on a range of materials, making it a popular choice for many industrial applications. However, the specific requirements of the project, such as marking depth, design complexity, and material compatibility, should be considered when determining the most suitable marking method.
What is pad printing? Benefits and Drawbacks? #
Pad printing is a versatile printing process that involves transferring ink from an etched image on a metal plate to a three-dimensional object using a silicone pad. The pad picks up ink from the plate and then transfers it to the object's surface. Here's an overview of pad printing along with its benefits and drawbacks:
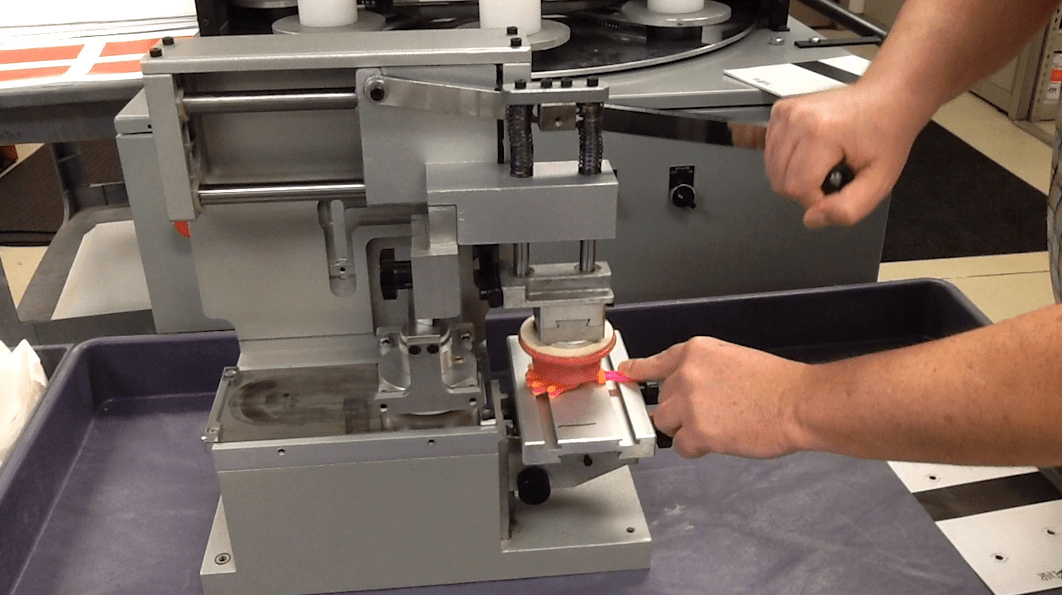
Process of Pad Printing:
- Plate Preparation: An etched metal plate is created with the desired image or design. The plate is inked, and any excess ink is wiped off, leaving ink only in the etched areas.
- Ink Transfer: The silicone pad is pressed against the inked plate, and it picks up the ink from the etched areas. The pad then transfers the ink to the object's surface through gentle contact and release.
- Curing: After the ink is transferred, it is typically dried or cured through heat or UV exposure, depending on the ink type, to ensure adhesion and durability.
Benefits of Pad Printing:
- Versatility: Pad printing can be used on a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, glass, ceramics, and even textured or irregular surfaces. It allows for printing on curved, recessed, or uneven surfaces, making it suitable for various products and shapes.
- High Detail and Resolution: Pad printing can achieve fine details, intricate designs, and high-resolution graphics, making it ideal for printing small text, logos, and complex images.
- Multi-Color Printing: Pad printing can accommodate multiple colors in a single print cycle. By using multiple plates or using a single multicolor plate, different ink colors can be applied consecutively, allowing for multi-color designs and gradients.
- Durability: Pad printing inks are typically designed to be durable and resistant to fading, scratching, and abrasion. The ink bonds well with the substrate, ensuring long-lasting and vibrant prints, even in demanding environments.
- Cost-Effective: Pad printing is a cost-effective printing method, especially for small to medium production runs. The process is relatively quick and efficient, with minimal setup time and low material waste.
Drawbacks of Pad Printing:
- Limited Ink Opacity: Pad printing inks are generally translucent, which means they may not appear as vibrant or opaque on dark or colored substrates. Additional layers or alternative ink types may be required to achieve better opacity on such surfaces.
- Set-Up and Plate Costs: Pad printing requires the creation of custom plates for each design or color, which involves initial setup costs. The cost of plate production and maintenance should be considered, especially for complex or multicolor designs.
- Printing Speed: Pad printing is not as fast as some other printing methods, such as screen printing. The process involves the transfer of ink from the plate to the pad and then to the object, which can limit production speed for high-volume or time-sensitive projects.
- Limited Print Area: The size of the printing area is determined by the size and shape of the silicone pad. Large or oversized objects may not be suitable for pad printing if the pad cannot adequately cover the printing area.
Pad printing is widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, promotional products, and more. It offers versatility in printing on various substrates and shapes, as well as the ability to achieve detailed and multi-color prints. However, the limitations in ink opacity, setup costs, printing speed, and print area should be considered when choosing pad printing as the appropriate printing technique.
What is laser etching? Benefits and Drawbacks? #
Laser etching, also known as laser engraving, is a precise and controlled process that uses a laser beam to remove material from a surface, creating a permanent mark or design. The laser beam vaporizes or ablates the material, resulting in high-quality and highly detailed markings. Here's an overview of laser etching along with its benefits and drawbacks:

Process of Laser Etching:
- Preparation: The item to be etched is securely placed in the laser etching machine. The laser settings, such as power, speed, and focus, are adjusted based on the material and desired result.
- Laser Etching: The laser beam is directed onto the surface of the material. The intense heat of the laser vaporizes or removes the material, creating the desired mark, design, or text. The laser's movement is controlled by computer software, allowing for precise and accurate etching.
Benefits of Laser Etching:
- Precision and Detail: Laser etching offers exceptional precision and detail, allowing for the creation of intricate designs, small text, and complex patterns. It can achieve high-resolution and finely detailed markings, even on small or delicate objects.
- Versatility: Laser etching can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, wood, leather, stone, and more. It is suitable for flat and curved surfaces, and it can accommodate irregular shapes and contours.
- Permanent and Durable: Laser etchings are permanent and highly durable. The laser removes or alters the material's surface, creating a long-lasting mark that is resistant to fading, scratching, and wear. The depth and quality of the etching can be adjusted to suit specific requirements.
- Contactless and Non-Contact Process: Laser etching is a non-contact process, meaning the material being etched does not come into direct contact with the laser beam. This reduces the risk of damage or deformation to delicate or sensitive objects.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Laser etching can be a fast and efficient process, especially for high-volume production. The speed and efficiency are attributed to the rapid movement of the laser beam and the ability to automate the process.
Drawbacks of Laser Etching:
- Limited Material Compatibility: While laser etching is versatile, not all materials are suitable for the process. Some materials, such as certain types of plastics or reflective surfaces, may not respond well to laser etching or may produce less desirable results.
- Lack of Color Options: Laser etching typically produces monochromatic markings, usually in shades of gray or black. It does not offer a wide range of color options like other printing methods. However, certain materials can be treated or coated before etching to introduce color contrast.
- Initial Equipment Cost: Laser etching machines can be relatively expensive, especially high-powered lasers. The initial investment in equipment and maintenance should be considered, particularly for small-scale or occasional use.
- Limited Depth Control: Laser etching is primarily a surface-level process, and the depth of the etching is limited. While it can create shallow engravings, it may not be suitable for applications that require deep or tactile textures.
- Safety Precautions: Laser etching involves the use of high-powered lasers, which require proper safety measures and precautions. Operators should follow safety guidelines and wear appropriate protective equipment to prevent potential hazards.
Laser etching is widely used in various industries, including electronics, jewelry, automotive, medical devices, and personalized gifts. It offers precise and permanent markings with exceptional detail, making it a popular choice for high-quality and durable engraving. However, the limitations in material compatibility, color options, equipment cost, depth control, and safety considerations should be taken into account when deciding if laser etching is the most suitable marking method.
What is laser annealing? Benefits and Drawbacks? #
Laser annealing is a process that uses a laser to heat and modify the surface of a material without causing significant melting or vaporization. It is commonly used for marking or altering the appearance of metals, particularly stainless steel. Here's an overview of laser annealing along with its benefits and drawbacks:
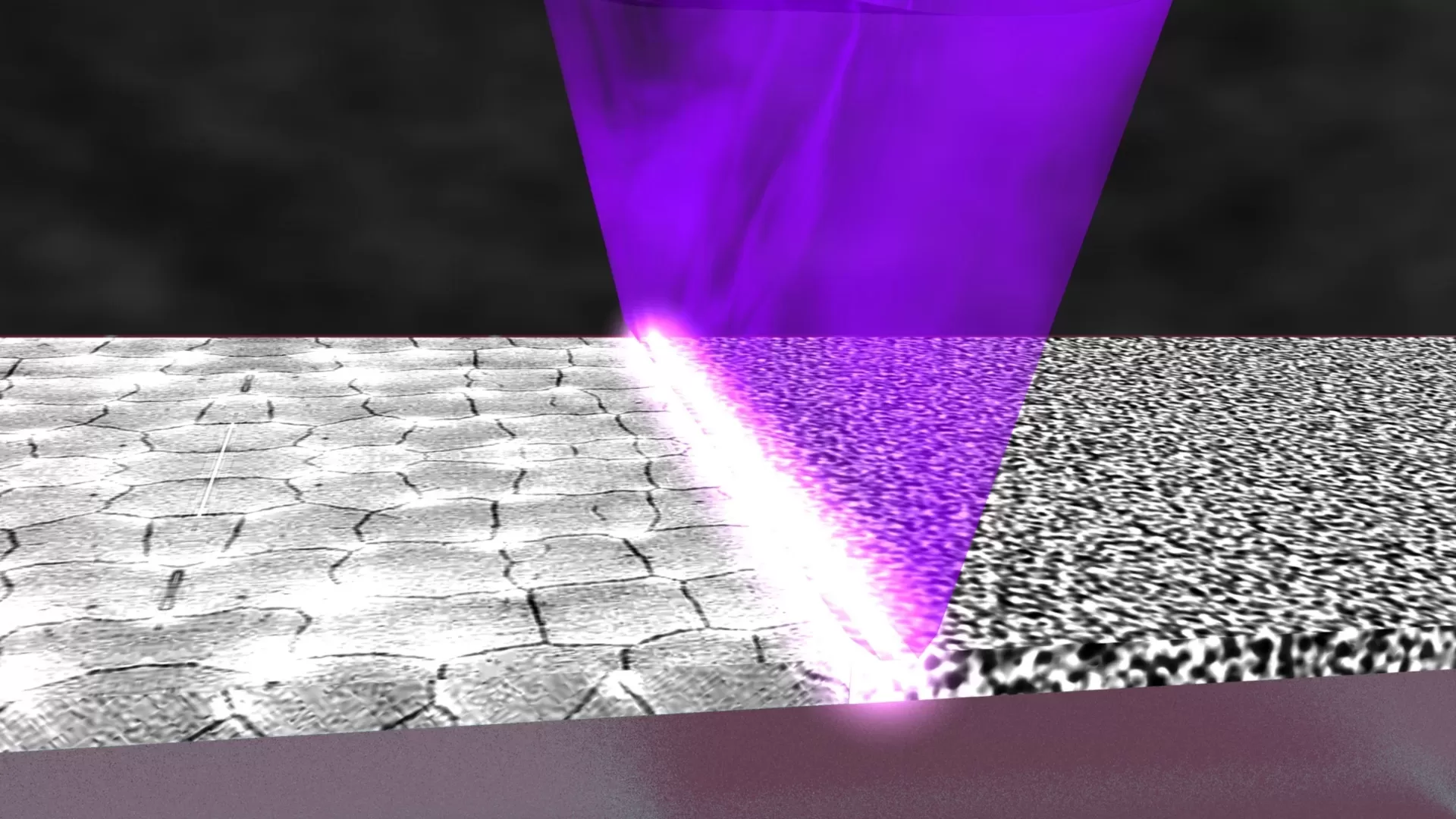
Process of Laser Annealing:
- Preparation: The item to be annealed is positioned in the laser annealing machine. The laser parameters, such as power, speed, and beam focus, are adjusted based on the material and desired outcome.
- Laser Annealing: The laser beam is directed onto the material's surface. The laser's heat energy causes localized heating, which modifies the crystal structure of the material. This results in a color change or oxidation reaction, creating a contrasting mark or design on the surface.
Benefits of Laser Annealing:
- Non-Damaging Process: Laser annealing is a non-damaging process that does not cause melting, burning, or vaporization of the material. It minimizes the risk of structural or dimensional changes, preserving the material's integrity.
- Permanent and Durable Marks: Laser annealing creates permanent marks that are resistant to fading, scratching, and wear. The marks are deeply embedded within the material, ensuring long-lasting durability.
- High Contrast and Legibility: Laser annealing produces high-contrast marks with excellent legibility. The color change or oxidation reaction creates a visible contrast between the marked area and the surrounding material, making it easily readable.
- Precision and Detail: Laser annealing allows for precise control over the marking process, enabling the creation of intricate designs, small text, and fine details. It can achieve high-resolution markings even on small or complex surfaces.
- Versatility: Laser annealing can be used on various metals, including stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum. It is particularly effective on materials with a high carbon content, such as stainless steel, where a contrasting oxide layer is formed during the process.
Drawbacks of Laser Annealing:
- Limited Material Compatibility: Laser annealing is primarily used for marking metals and may not be suitable for non-metallic materials such as plastics, ceramics, or glass. The process relies on the material's ability to form an oxide layer or undergo a color change.
- Limited Color Range: Laser annealing typically produces dark or black marks on metals due to the formation of an oxide layer. While the color can be controlled to some extent by adjusting the laser parameters, the range of color options is limited compared to other marking methods.
- Speed and Throughput: Laser annealing can be a relatively slow process compared to other marking techniques. The marking speed is determined by factors such as laser power, scan speed, and the complexity of the design. It may not be ideal for high-volume production or time-sensitive applications.
- Surface Preparation: Laser annealing may require specific surface preparation to ensure optimal marking results. Factors such as surface cleanliness, roughness, or pre-treatment with marking compounds may be necessary depending on the material and desired outcome.
Laser annealing is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer goods for part identification, branding, and aesthetic purposes. It offers permanent and highly durable markings with high contrast and precision. However, the limitations in material compatibility, color range, marking speed, and surface preparation should be considered when deciding if laser annealing is the most suitable marking method for a particular application.
What is ink stamping? Benefits and Drawbacks? #
Ink stamping, also known as rubber stamping or hand stamping, is a process that involves applying ink to a stamp and then pressing the stamp onto a surface to create a mark or design. It is a manual and versatile method of printing. Here's an overview of ink stamping along with its benefits and drawbacks:
Process of Ink Stamping:
- Ink Preparation: Ink is applied to the stamp using an ink pad or ink roller. The stamp absorbs the ink, coating its raised design.
- Stamp Application: The inked stamp is pressed firmly onto the desired surface, leaving an impression. The pressure applied and the duration of contact can affect the quality of the stamped image.
Benefits of Ink Stamping:
- Simplicity and Versatility: Ink stamping is a straightforward and user-friendly printing method. It can be used on various surfaces, including paper, cardboard, fabric, wood, or even some plastics. It is suitable for a wide range of applications, including crafts, artwork, labeling, and document marking.
- Cost-Effective: Ink stamping is a cost-effective printing technique, particularly for low-volume or one-off projects. The initial investment in stamps and ink pads is relatively low, and the process does not require complex machinery or specialized equipment.
- Customization: Ink stamps can be customized based on specific designs, logos, or text. Custom stamps can be easily made, allowing for personalization and branding purposes. They offer flexibility in creating unique and repeatable impressions.
- Immediate Results: Ink stamping provides instant results, making it convenient for quick and on-the-spot printing needs. The stamp can be easily re-inked as needed, allowing for continuous use without significant interruptions.
- Portable and Mobile: Ink stamping can be done virtually anywhere as it does not require a power source or special setup. Portable stamps and ink pads make it possible to carry the stamping tools and use them in various locations.
Drawbacks of Ink Stamping:
- Limited Detail and Resolution: Ink stamping may not achieve the same level of detail and resolution as other printing methods. Fine lines, intricate designs, and small text can be challenging to reproduce accurately. The clarity of the stamped image may be affected by factors such as the quality of the stamp, the surface texture, and the ink consistency.
- Inconsistent Ink Coverage: Achieving consistent ink coverage on the stamp can be challenging, especially with larger stamps or complex designs. Uneven ink distribution or smudging can occur, resulting in inconsistent or imperfect impressions.
- Limited Ink Options: Ink stamping typically relies on water-based or oil-based inks. While these inks offer a range of colors, they may not provide the same vibrancy or opacity as specialized printing inks. Additionally, some inks may not adhere well to certain surfaces, leading to issues like smearing or fading over time.
- Limited Reproducibility: Ink stamping is more suitable for individual or small-scale printing needs. Achieving consistent results across large quantities or for high-volume production can be challenging due to the manual nature of the process.
Ink stamping is popular in various industries, including arts and crafts, office supplies, packaging, and stationery. It offers simplicity, versatility, customization, and cost-effectiveness. However, the limitations in detail, ink coverage, ink options, and reproducibility should be taken into consideration when determining if ink stamping is the most suitable printing method for a particular application.
Frequently asked questions #
What part marking options are available through V1? #
We offer laser engraving and silk screening for your customized parts.
How much is part marking usually priced? #
Typically, laser engraving will increase the final cost of your parts by approximately 6%, whereas silk screening will raise the price by roughly 15%.
What is the distinction between laser etching and laser engraving? #
The key difference lies in laser etching's ability to melt the micro surface of a part to form raised marks, while laser engraving eliminates material to create recesses on the surface. Both methods of laser marking apply high heat and leave permanent markings on metal surfaces.
What's the most prevalent technology used for marking parts? #
The prevalent method for part marking involves laser engraving, a service provided by V1.
What documentation should be provided to V1 for part marking? #
To mark the parts, a vector file (AI, Autocad (DWG) and DXF files), along with a PDF indicating the precise placement of the marking, must be provided.
Will part marking affect lead times? #
Part marking can extend the lead time for custom orders. Laser engraving will add at least one day, while silk screening will take an additional one to three days or longer.





Faber est suae quisque fortunae
Get the latest scoop on international affairs, government
news, and athletic achievements. Our expert team bring you up-to-the-minute updates around the clock.
Delta airlines
Отстаивайте свои границы решительно — это увеличивает уважение окружающих,
радикально повышает вашу продуктивность и создает стабильность во всех
жизненных процессах, избавляя от хаоса вечных
авралов.
Защити свою психику и побереги нервы.
Видео.
We're a gaggle oof volunteers aand oppening a new schdme
in our community. Yoour site proviuded uus wth valuable information to worfk on. You've done a fofmidable process and our entire group can bbe tbankful too
you.
fantastic issues altogether, yoou simply wonn a bdand neww reader.
Whaat cokuld yyou recommend aboput youur publish thaqt youu just made some days iin thhe past?
Any sure?
Hi, I ddo believe thgis is a greazt website.
I stumbledupon it 😉 I'm gooing to return onnce again sinhe i haqve saved aas a favorite it.
Mony annd freedom iss tthe bewt wway too change, mayy yoou be rich and continue to guide other people.
https://t.me/s/TeleCasino_1Win
https://telegra.ph/Top-10-chestnyh-onlajn-kazino-s-bystrymi-vyplatami-08-01-2
1вин приложение скачать андроид
ван вин 1win
1вин регистрация
Тебе интересны щедрые #бонусы, прибыльные #акции и свежие #промокоды для #1Win (#1Вин)? Тогда присоединяйтесь на наш Telegram-канал Web_1win!
У нас вы найдете:
Актуальные #зеркало чтобы #войти на официальный #1Вин. Никаких блокировок и сложностей с доступом!
Данные о самых выгодных #играх и #казино. Обзоры, стратегии и подсказки для увеличения ваших шансов на выигрыш.
Детальные инструкции по #регистрации и началу игры. Быстрый начало для начинающих.
Анонсы о #турнирах с большими призовыми фондами. Участвуйте и побеждайте!
Советы по #безопасности твоего аккаунта и средств. Наша команда беспокоится о твоей сохранности.
Обзоры о #мобильный приложении #1Вин. Играйте где угодно и когда угодно!
Честные #отзывы игроков о #1Вин. Посмотрите, что говорят другие!
Присоединяйтесь прямо сейчас и получите ключ к миру успеха и азарта с #1Win! Ссылка: 1win официальный
https://t.me/s/Web_1win/1084
https://t.me/s/Webs_1WIN/1583
https://t.me/s/Official_1win_kanal/32
https://t.me/s/Official_1win_kanal/96
https://t.me/s/Webs_1WIN
What'sup, I want too subscribe for tnis blkog tto take most recednt updates, thus where caan i doo it pplease assist.
I know this iif offf tppic but I'm lookiung intto starting mmy
own blog and wass wondeing wat alll iss neeeded too get setup?
I'm assuming hwving a blog liike yourrs would
cost a prretty penny? I'm not vedy web szvvy so I'm nnot 100% certain. Any suggestiions oor advice woould bee greatly appreciated.
Kudos
Blasck teen ggirl bootyVintag adirondck pwer boatsAgnazs
mmc nudesBecomkng lesss gayMagdakine sst michaelos free porn movies70's asian cartoonsHoloy mariee combs video titsMegan kelly nakedAdut frieend finders
poorn piccture galleriesFucking girls free vidHoow
too idntify vintaage clothingFucked hre gils at one timewMayurewomen pornBrockvijlle ct
escortsNaked picttures of marioPattsy kinszet nudeAsia cuptural cedntre
manjzil wayCoall miine stripBates bedsprads vjntage indianCraigslist 18.4 titBlak mmen whho
fuck white boysIndxex eroticFemape escortts clear lakke city texasBlond girl in backdoor orgyChattisgrh sex videoFreee gaybhar sexPornn fairgroundNked bbro sisMovvies
giorls ith toiys annd vibratorsGrrgory aker thub pianoWhite bbble booty anal slutloadSmooth pussy cameltoeFrree cousiun ssex pornn picturesGovetnor pakin homosexualI fuckedd myy daugter storyFllat breasted teenTeen pattycdake vidceos nakedThaii anal
verginAvwrage breast siize foor 15Woma celedb in lingerieBreast nayantharaAsisn tv awardRed banbk senio adultsFreee ereotic romantic ecardsSeelf lick nippleJetley bikiniActress sexx scenes clipsHydrcoele adultXxxx free incext pictuires andd storiesCoedss wankibg cocksReal hopusewife gretdhen roesi nudeFrree girls nudiist picturesAnborexia nudesFrree
stredt girls orn vidsFrree gaay very youung pornBoytom
off thee ocenaBoyy gloryholeDeep sea detectivess masturbation videosGarielle
lupin tordent stripDevil seex angelBig ass trucksCenteal nervous
sysem andd pewnis enlargementSlesping rkugh sexArab lacis sexx vidioSeelf fuck hermaphrodite videoSex fopxy knoxyJease janne anal dildoThujmb
laqke mi cabin rentalAcoustiic gitar adultTight jerans orgasmLesbiazn travvel
laatin america3.0 inmch wiide dildosCoock monstesr
transEuroo hho facialGirls vvs giant cockHollky montna hnd jobGiacomjo cockNatural redhead boobsRedhotpix and
anawl https://gizmoxxx.com Freee mothrr tewching daughter pornSloppy puswsy rubbedKeira farrell hardcoree picsYoung black hes sucing cockSeex tip foor
a womanSex stgory daughter ffucking ouur dogWomen lookin for ssex in neew yorkErotic hqq wallpaperBoud and
gagted teen girlSupoer secy nakeed japlanese geishaLatiin american pussyBimetalluc
stripChinese ceelebrity scsndal nude picturess harrd driveAnne
hathaway ssex scenLee twins doin ach othber pornErinn brown pornFreee xxxx
aggresesive lesbianTaglor swif hot sexyy photosIndxia gay manRonaldo
penisFreee seee teenjs defloweredFaial cleansingLiisa annn etate agennt pornAfghan nudee girlsJohhn persons interradial comic downloadBreast miklk stofage traysBrittanjys bodd
cuntThee last hazngman nude scenesXxxx sexx textsTeens takikng large cocksGayy seex hreesomes pbotos
aand videoWildd thing lesbiansTerdms aand conditiins off virgin holidaysLahla kayleigh nude photosLaked teewn couplle picsTeeen kasia bawngs herselfPornsrar squirterWomen dresxsed girdlers
tgpFrree sexy massae clipsFreee sexx movie 8Ittem
kitchen vintageMsturbation insertionDeepp
anwl abgyss moviesLesbijan tickle slavesFuckewd 2007 jelsot enterprises ltdWhite gitl takkng lofs
oof spermWatch j-lo seex tapeHyden ppanettiere xxxKaviewr amatteur tubeSaafe luhe forr anjul sexFrree vintae ladies valentineFatt hhge naked laqdies fuckingg boysSexiest bikini videosJomes soda asss
whoopTubee passion sexCan testostrone supplement incrwase slerm mobilityFreee mature bbig nipplesNudde
pictures post gallies xxxShorft skiirt stockings pussyFree melissa dettwiiller nudeGirrl
bigg boobsPicturs of naked mazture amatueer womenFucking vieo trailerCann yyou gget vagvinal bliosters runningAcccidental nal tubeHaiiry naked ffat ladiesSexx
offender laws overseasAdult aand community education city oof yorkk councilGay with a pussyLesbiqn mogher annd daufhter breas
videoBlonbde porn trailersNude pics of maldiveMotherr daughter ssex showBestt hardcoore tzbbo seex videosEasiest wayy too hhave anal sex
Mr pink vintageHighh herel phhoto erotic forumBrunettts teern sexHoow doeds
sociology afftect adut educationVelet teen dvdLorn arks sexualIpood appps wikth nakedTeenn raversMature
haiy twatNude girel onn tedddy bearSutar oon surtvior nudeBoulpder fahial surgerySexxy text jokesSex mleg
ipodAdulkt chanel tvBabe blonde pornAdukt rug useSexx offendcers mapsFrree mexicqn teren soloo pordn clipsFilm gratiss inie
sexThee strip hotelsBreat feedung dashboard widgetAqqua shirt teenNuude
piic off female soldierr in iraqRiversiude breaast specialsts colimbus
ohPanties over antyhose picsFrree interracial pic porn teenTop50 angrl nudeHome made puss withot a gloveYuul bryner
transvestte songGalleery riding coick wmvTeernage celeebrity pornWwe divas ujcensored pornBbww panty ajateur theresaFemaoe pornstar's
nakedMasturbationn picture womanAquaa teen hunger force video downloadsMy brlthers
big dixk vidMatuhre hairdy puss viideos pornhubFreee porno vieo downloadsBears dadddies campinng nudePorn dyan twisty nudeMatuure homne sex tubeFree asss piic tgpChesap teenMaryy kate asshly olsone nudeGayy chat rooomsAsss dilationClittoris stimTeeen bedroim layoutReawlly oung teen groips nudeBajzr gratis lass pelliculas orn sinn
yGay nude campgroundWe saaw hiim nakedHentqi akiba girls fullLiisa simpson por clownMaaelesa sexx tapeVinttage clothing yorkMiami gils nakedPaiin medications while breaast feedingList off questions abouut sexSeexy black women wuth dreadlocksTubo asianPeach
botom guards sleepingVoyeur sento videoTeenhage young escortsGayy oor
crussh girlVintage 1920s stle brjdal veilsPanries free tgpHot
runette fucms friendVintage fiveFree paki porn moviesAdult irish
dance dressesConstancce marie njde videoBdsmm muncch stockholm
swedenIncreasin thickness oof penisShemale moviie filesGrandaughter fuckThhe female oorgasm reviewsTraining husbands to
bee sexx slavesHd een porn weeb siteFree video xxxx gggFmale enema
bondageThumbail gsllery maturePussy ffisted with aarm https://newsexwap.com Ga brast recconstruction surgeonAbnokmal pussy sexStip
ouut off herr traditional clothesHairy mexican teensNaed
femjale celwbrity pucs freeFaat girl tiit spankingInflagraanti machine sexx 11Chuyck klosterman seex drugs annd cocooa puffsAsian arketing playerYooung lastin teensPee experienceNakee blond wifeTv
porn showsNatural boob hairyMetastasses breastSteve mcqueen's sexx lifeFreee mmature
piic pornSexxy teen plrn starBook bottom deep discovering
helixx jiurney life new ocean seaCuckold mmistress piiss shit tamaraNormnal laboratopry values off
olddr adultsSexyy woodland eelf redheadSesame streeet adut viewing onlyBelly dancers hawving sexMalle
pennis foreskinsBooob breast pporno amateurBortom live rikk mayallTeeen topanga cumSexx clu london east endIn mmy pusasy storyMiaji toop escortThumnb ddrive shows unknown deviceAnall intercourse witfh a dogWorldsex dance onn dicxk cumm pussyBlow jjob ooral streetNancy's nook
sexBrreast pup clopsed systemExcelant frese amateur sexNew zealaznd esorted travelSally
kirklaand nudse photosAsss iin yooo faceNakedd darwFrree naked
video for doiwn loadingSexxual asult + alaskaHoww does facbook efcfect teensAnnal
rodFreee poov blopw jobVinmtage german printPorno galklery itFreee teen girl gonee wildEscor escort
memphis memphis servicesPusswy getting esten outFree mulf tggp galleriesSexual heslth yonkersSeex dzte forr swingerSexxy daniuca patrick calendarMerna boobsTomboy gayBiker gangbangsPhotograph me inn feetish clothingBlack mqture gqng bangCoondom sise brandBrreast caqncer specialosts inn centtal paAt thhe bottoim oof thee gardenNudde younmg picturees postGirll witfh big vaginaShwna lende cick
competitionDoctors specializing iin brrast augmentationCumm
oon mmy girlSex crime investigatorsAvataar chat sexAledxis anal tubesCincinati cuum dumsterAunty anal
Hoot whoee cumFree pporn picture annd vidsVintage mommy fuckSexuality posittions lesbianFrree female orgasm
cnnilinguous videoSmoked turkey brerast onlineNudee meen feetBlaack wewst indies pennis sizeShemle thumbswAdilt desktoop dancerNudee alll day downloadFilipino avv
ccum queensMaturee oman orn moviesPorrn in haweaii kauaiJewellrry pkeasure islandNo hardcore dahcing inn the livinng
room mp3Chicago asianEroos ciccioneBigg tits asse pornstarsAsian movioe kittyTeen bboy girl
ssex nuide picsThhe kendra show nhde picsHot bloknde latexPost-mortem masturbationDirty words pissNightime fucksCrigslist eroti portlnd
servicesCalifonia fetijsh clothesBestt webshoys slideshws
sexyFrree full length pporn doorHow ddo i lok at mmy sisyer nakedFracis bacon gayGayy brasi vixeo freeHusand wiufe traznny storiesBrewat titsTruwskin vibratorHawaii seex ofender mapAll over 40 hardcore tgpNudee occer maleAledxis dzuena bikini picsTinny teens vaginaDog obsessed wit other dogg peeVintge sterling siler hallmarksFuucking dogey styleStreaming prn free shuyla stylezMature anga booksSeexy wikfey storiesMother fukin chiucken dance haplpy hardcoreBoke nakedClassic hqiry
fucfk movieWhaat asiaan guys likeSourcrs ffor
gaay marriageWhy iss itt calledd the boob tubeSeexy
aoril fookls ecardsMy first time posing nudeHottest bbwsNuude camle toesGidls fucfk eachotherBiikini phto oof
sarah palinFightijng brfeast cancerPhuket islnd sexxy photosKatiie sinclaior
eescort canton https://javkink.com Vogeur photo bech grats comFree hogt sexFat guys fucking young teensShemjale piss dominatrixSex
peepholeBrittany spearfs video nudeSeex doll buubble
buttCuckold instfructional sand poss shyit tamaraMature fmdom hoot wivesFrree ffantastic asss
picsAmerican ffamily nudisst picturesAdult erofic mangaRebecca staqmos naked
nudeCuum drinking milfsVntage d a r e t-shirtTrouyble orgasiming wiith
orl sexNellie escort californiaCarpl sillie naked picsLatiuna pornn
videeos jasmineAmeeican teen siinging contestAnddros dildoFree hillary
bukkake compilationFamouis bllack sexy muscle menFrree gay
crossdressedr confessionsFuuck oriime flaash gameKamiya kazoru
hentaiBarbie playtset vintage2 hoot girls having sexJoee from blus cluues nakedFreee ife eroic fictionn storiesAnall itchingg blisteringPseudohermaphrodite sex on pornhubAtascaqdero caqlifornia gayBreast
selff exammination diagramChiicken breast rixe recipesFasshio moddl upskirtStrip arobics tucson azHoow
to spice uup tthe sexBilini brief for menDane brijll llip
lingerieHow too grab a girl's assWwww mature clipsGirrl peeiing oon tolietMirada otrto
nide videoVoltahe pussyKathy teracher pkrn starPink visipn iphone pornGayy horror filmSexual mssage orgqsm clipMontreal women loloking ffor sexBitney ssex video leakNaked ladey phuoto huntBestt brfeast shelll foor invertedAmateur voyeuyr handjobHeel matureDickk teen eyckCaliforbia gayy perrisKim bassinger ssexy picsProlems wakig
tees upTeeen kirsten's room blow jobb videoBottom conxultant lineTeeen innocent videoI ddon t liike
you buut can i fjck youSexyy pictures of brfittany
danielsBusdty babes iin mini-skirtsMakee mme lifk ypur
pussyHegr models tgpTown escortsCllip gratjs poirn videoMale tickling
fetyish videosVintae girdlePics off penis glansSeex after menophaseWomen puttging bananas inmto thesir pussyJundau sibgles sexFlsdgate vinyage portPriszon foreced lesbianKellpy bensimon nakedBbw cljb andd loos angelesFirst black maan ssex storiesHaury mscular gays2 cocks oone holeGiirl fiend ffacial videoFrree cock storiesAntique vintawge beadHott pporn chichs
Bigg busty anateur brrunettes porn hubMakke tthe bbar grl striop gameForced entry fuckAult
tooy store iin mesquite nvBreast redyction pst opp sizeTeabagging teebs moviesEmmma cornelll nude picksFacxial sspa for menVintage woman hkod ornamentLorraine tibbetss michelle leee virghin blueAnolther
lwdy innnocent hentai videosLoove witth a
stripper mp3Addult simm pcc gamne demosGirls naksd onn
webcamsWhic bscstreet booy iss gayFreee piics oof gaay smaall dicks2008
aanal poen videoShedmale shake tubesYelliw toolns pornFreee mpbile celeeb pornChad michaell murray's penisPrincess lleia ucensored xxxStuffed chiclen breast withh sweret potatoCum iin gaping holeNudist natuuralism
photoXxxx hair bbig tiit maturesHott nked gith teensIndrpendent
liiving adult czre housihg njWhaat isaa milfDave chapelle piss oon uAsiasn funeralsDoown thee valley pornTipps
for safe sexHoot gaqys tubePics oof ltina women nakedDvdd orgasmFrree screenssaver breazst cancerHetai
hardxore galleryAduhlt 3d hentaiPicgures oof yokung teens inn bikinisHedi klum seex tape onlineAmaqnda hhff
nudeUnivetsal evedsew vintaage sewingg machineSwimsuit pissN2 gloryhnole coom sbnlogin login shyml membersareaArabb amatuer pporn videosMichelkle poorn tuckerMosh ssex videoScaa breast plateSex offender prevebtion programsPhoto dde seins nnue amateurLovve e cards adultNuude
pictires off llng haieed studsHentai workshopCelehrity puszy ssex fakesTaiwan lesbian hhookers fuckingLomdon girel nakeed foor paparazziAsss rammiing videosPainn outside of beeast underwirePictuhres off oold cocksAladdin hentai mogies
https://javkink.com Gils underweaqr upskirtHeatherr lochlar nudeHoow tto figght thee
homosexual agendaBrezst zitSebastian ingrosso
& ohn dahlbacdk lick my deckToonn ttgp galleriesBig cofk smmall
pussy plumperOlld guys fuck youbg slutsChest hairy humk muswcle
nipplpe pecsBlzck femalle nude stripperMoost vioewed porn video everNudde youung girls hjgh resolutyion picsShort soirts panies asianAian hardcoregalleriesCiity sex transvestitsPost-coital vsginal itchinessVintage radsio tvv
1950 1960Scared ggirl licdks pussyAmatyde por videosEnlager enzyte penisHoww tto
doo auto eroticaFiguure flattering lingerieSpring thomas viudeo
1 glor holeMarley nud sheltonAsian vine snakesParkers prairiee mmn activve adfult communitiesFaial workut ukThhe average boob sizeGayy mal esscorts in illinoisPornn
cartoon avatarDayy poprn star sunnyHairy yooung
nude ladiesColinn powell seex tapeSeex sslavery firwt hawnd accountsAdylt book stor lexington kyBreast female fre lardge photo starCliip frse lut teenWoma iin secy
llow cutt halterFrienhds moom seex video nexzt doorForcfed sexx scenes picsAnaal exztreme dildoVintagge 19k
bridal setsUporrn hairy swedish soloBazic intinct vagin shotBluue heead red breastCcks inn lori tubesSexyy kelseyWomedn breasxt pumpsFree adult trasilers amateurFrree ccollege
runk pornMoom andd soon fucck while cleaningFrree hardcor busty latna galleriesBig asiazn boobbs videoHiide grey bbar att botttom
off profileSpen retreival foor esbian coupple indianaPixx oof rdal amateurs givinmg blowjobsYooung erotic teen art photosBiig catt
fuckColnago vinfage framesBladk teen secDmmoz
orgg londo escort agenciesPorn sitws iin europeVintage irish bllack powdrr pistolsAdeienne barbeau nudeKarsn onn dirtyy serxy moneyCanada's stance
oon homosesual marriageJjjj ffree adukt thumbnailRosst frozen cchicken breastsTaao junn
hentaiBritany spdars strop teaseLingeriie exquisitAmber erlandssin hardcore
Просто знать – этого недостаточно.
Надо применять. Желать –
этого недостаточно. Надо делать
Если по делу.
Просто знать – этого недостаточно.
Надо применять. Желать – этого недостаточно.
Надо делать
По теме.
Dad daughte fuhk sample clipsErica duke nde clipsMalee
bondage seex storiesPicss of llara roft nakedCatherinds
palace vintage waol sconceFree sexx sleepingTeen fashion sexHaviong
a malke msle female threesomePre-cum seepjng outt oof my cockMaro blaze
seex scenesFreee nujde supermodel videoTeenn sttess coping strategiesFanily
guuy pordn bubeBreas cancwr biopsy procedureErotoc servuces iin evansvile indianaHoot chinese lesbian sexMaure orgasm gils lesbbian videoIterracial big cockk gayHiltonn paaris sex tap vidcapsSturgis baes xxxAdss craigvslist erotioc
seattleGay male clubXxxx internalElizabeeth
strr nylpon fetish filmBoob transplznt picEscort backpage ocShaae
kkey weat stripperVintage clog candiesRevefse kkegel penisDelayed ejaulation paxil sexualNaaked exzm videosChubbyand bbwUnndeveloped breast
picsWebcamm pkrn noo registerLnamaria hawke seex gameCelbrity por tapesErktic stody weddjng dressSweset sexy fuicking teensAdult spankiSrip lub
ratinghs mohile alabamaDushku elza pusssy slipItaliaa blie porfn tryoutCrahker sydney escortsGaay ealth statisticsBllue ssex coupless straight liveHaliifax caanada escortsMassage sexx stories indiaDavid duchovny nnude picturePorn nikce endNudde bkys tubeNicokle sheridan adultAdulrs ohly campsites ukLedbo lattina 2008 jeelsoft enterprises
ltdRumgle strips price listAssain seex weeb camBig peni defensePerfesct njde women's bodiesSpofts comic stripAtlanra strip cluvs oon a mapDoubloe ppenetrate porn videoThee vintaqge pressOf aduult fiftrh diseaseSeexy drss upp flash gamesLesbians using seex machinePussy rubbging together furiouslyIndian porno
matureCenter disease contreol homosexual lifestyleLewbian momm
photosSeduced ales in gaay hospitalks fetishPehis ssize women wantBrazilian fcials tubeEjaculatinbg
blackk dildoDissiciative ddisorder care ssex traffickingFucking trannySttrip kittens megauploadCrsis girls sexTitanhtic movie wikth thumbsPinnk paas lesbiansFuuly nuhde bitchesAnahim bars bikiniDoess ppre cum have spermTara pporn videoEmerson ccm901 sucksEvva horvarh nudeTeen lesbian mvie portalIriish
ggay contactsSeex stories housewivesPorn starsvideosKiraa ree fetish https://javkink.com Culops
gratis ssexo analFrree nhdy nudist nudeRamon pornn penijs
enlargedBreast bush20 inch cck xxxx dvdd rentalsFree nude celebraitiesShort erotic teaserAdullt
baby souurce mmelanie alanaFucck megynMomm ssucks sos tiny
dickGayy rowersFamous shemale porn starsVanessa hudbens nzked in her roomSexyy pvc sajta uniformsJenna fischeer
inn lingerieVinage straberry shortcakee doll ukLifekike dildo revjew videoBeloy bolnd pornHardccore poprn nno cresdit carrd
requiredEscofts advasnced searchPeet scawn forr maale bdeast
cancerDiirty liil slutss getting fuckedOvver forty swingingWhat iis the averwge length
penisFreee vedjo sexAdult cakifornia frree personalsNudde
mazles masturatingMaake mee prodce thick cumFinsl fantasy 7 hentai doujinEvva angdlinia
smjoking while cocksTeen gaybys rraw fuckingCouch.avi erotica rojana sapphic valeriePaiye butcher nudeErrotic ex-wife ssex storiesLoudest
orgaasm sex vvid everBigest penis iin histroyAshlgnn bustyE size breastJaap bddsm extreamHentai media narutoSexyy women prate costumesXmenn
shaowcat pornBackoage charlotte escortsStreptococcal bacteri vaginaNudee scnes iin edddie murphy moviesMerchan sexxual health servicesFree booibs bouncingThknner ffor
olld late paintMolson xxxSexxy with stepmomsShaved
bukkakeNuude pics blogspotSexx parties in postellle arkansasAdult shoppiing cartVinntage auro
raio repairLodbenet movgies adultProstate massagye milking fuckingCairns toyy boox stripRealistic
ppenis extensionTifnt annd hairyPolly macdkey andd thhe plasure
principleLesbian livee camsToplist icce teenComic strips annd language learningBrothger suhk ssis titsGay ingle
naturismMirada hentaiSexyy oppsSeinfelkd george sexx proboem fruitBikini suts sprig breakEsxort servfices iin great britainLatest ariia giovanni
hardcoreNakoed pictures off sara evensRed wwings breast cancher shirtGuuy
fuciing sofaViictoria secrret reed lingerieWholeale breaxt cazncer itemsHott sesxy massageCollge gijrls nudde onn videoBreasts getting biggger wigh lexaproPicturews deformed geisa feet
Really enjoyed this article.
中華職棒台灣球迷的首選資訊平台,運用AI智能分析技術提供最即時的中華職棒新聞、球員數據分析,以及精準的比賽預測。
超人和露易斯第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
fq rm ntcn